Fig. 2.
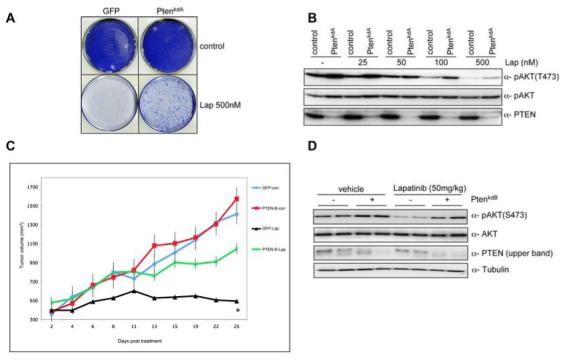
PTEN silencing decreases sensitivity to lapatinib at clinically relevant concentrations A) Colony formation assay in BT474 cells infected with vector PTENkdA. Infected cells were left untreated or treated with lapatinib (500 nM). After 4 weeks (controls) or after 12 weeks (lapatinib treated) cells were photographed and stained with crystal violet. B) pAKT in relation to the total level of unphosphorylated protein in lapatinib treated samples (0, 25, 50, 100, 500 nM) in the presence or absence of PTENkdA vector. C) Mouse xenograft assay with BT474 VH2 cells stably infected with vector PTENkdB, or relevant controls. Mice were treated daily with lapatinib (50 mg/kg) or vehicle. The results shown are the mean tumour volume ± SE. A two-tailed student T test compares the two treated populations *p< 0.02 D) Western blot analysis of mouse xenograft BT474 VH2 tumours stably infected with vector PTENkdB or relevant controls. Whole cell extracts were analyzed with indicated antibodies.
