Figure 3.
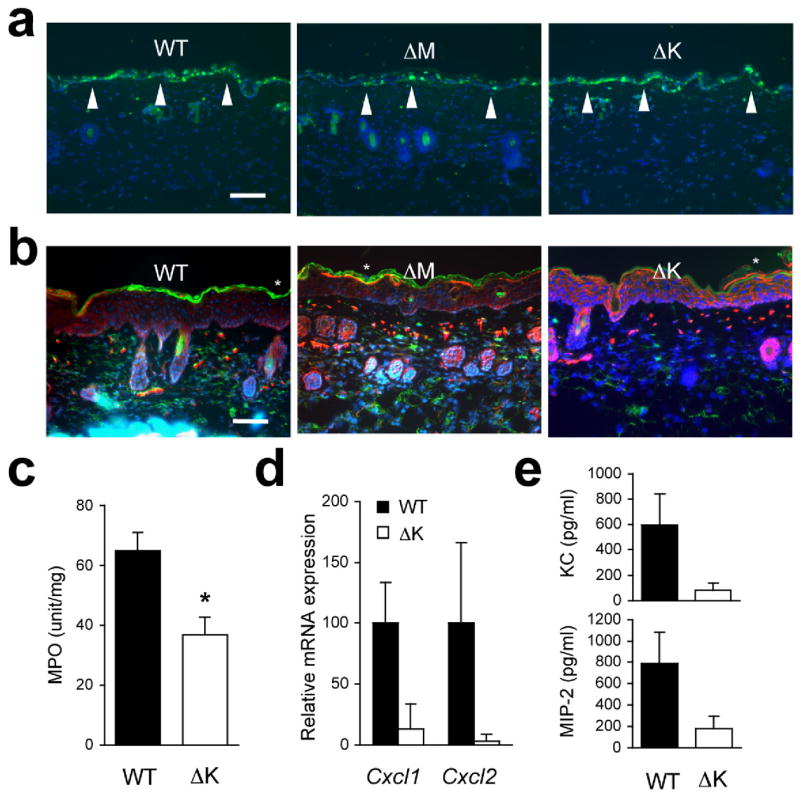
UVB-induced inflammatory infiltration and injury depend on epithelial p38α signaling. The shaved back skin of mice was irradiated with UVB (160 mJ/cm2) to induce epidermal injury (a–d).
(a, b) Skin tissue sections from the indicated mice were analyzed by TUNEL staining 24 h post-irradiation (a) and immunostaining with Gr-1-specific antibody 96 h post-irradiation (b). Scale bar, 100 μm. Apoptotic nuclei and neutrophils (green) are shown together with the counter staining of DNA (blue) and/or F-actin (red). Arrowheads (white) indicate TUNEL-positive nuclei. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.
(c, d) Skin tissues from the indicated mice were analyzed for MPO activity (n=4; *P = 0.015) (c) and gene expression (n=3) (d) 96 h after irradiation. Relative mRNA expression was determined by qPCR.
(e) Culture supernatants of the indicated keratinocytes were collected 6 h after UVB irradiation, and KC and MIP-2 concentrations were measured. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
