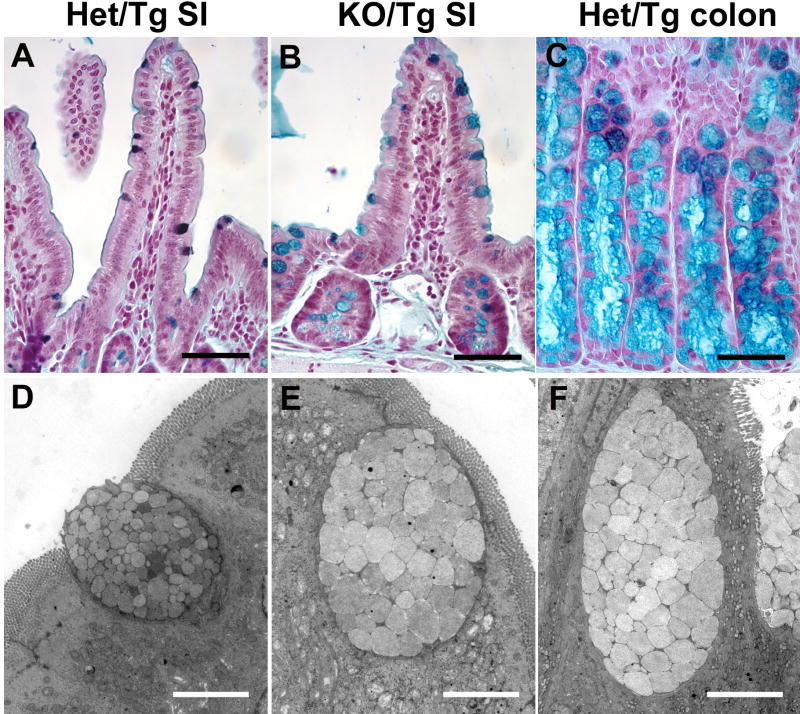
Figure 4. KO/Tg distal small intestines lose small intestinal features and exhibit characteristics of colon.
(A-C) High iron diamine staining of intestine. Most control distal small intestine goblet cells contained sulfomucin (dark brown in A), whereas most KO/Tg distal small intestine goblet cells contained sialomucin (blue in B), which is characteristic of colonic goblet cells (blue in C). (D-F) Transmission electron micrographs of goblet cells. The goblet cell in the KO/Tg distal small intestine (E) and wild-type colon (F) are similar; both contain larger and more electron lucent granules than those in goblet cells from normal distal small intestine (D). Bars, 50 μm (A-C); 4 μm (D-F).