Figure 5.
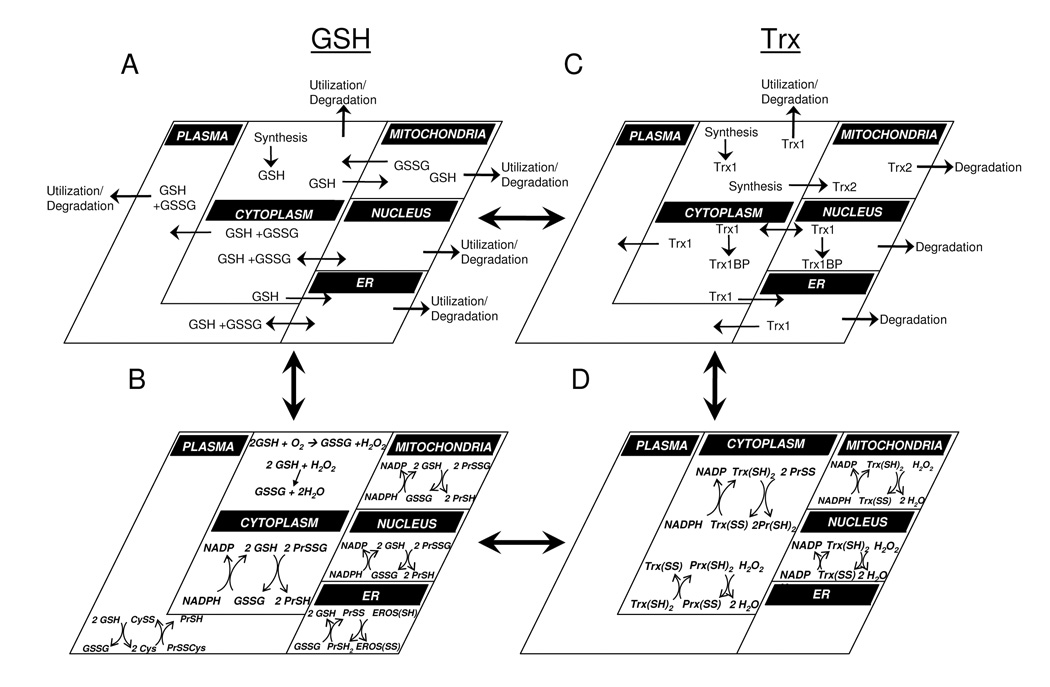
Complex redox systems maps can be assembled from models for redox couples in different compartments. The steady-state flux model for GSH and GSSG (Panel A) can be combined with compartmental models for oxidation/reduction of GSH/GSSG (Panel B) to provide a more complex model including synthesis/degradation and transport along with redox processes. Similar models can be developed for thioredoxins (Panels C, D), and these can be combined with A and B to provide more complex descriptions of interacting redox systems. Such models can then be used to analyze cellular control of sulfur switches, linking redox changes to specific sensor and rheostat functions. In this simplified model, only GSH and Trx couples are illustrated; however, these concepts can be extended to NADPH/NADP+, peroxiredoxins, Cys/CySS and other redox couples. For illustrative purposes, peroxiredoxin reactions are only depicted in the cytosol, but are present in the nucleus and mitochondria as well.
