Figure 1. RORα is highly expressed in TH17 cells.
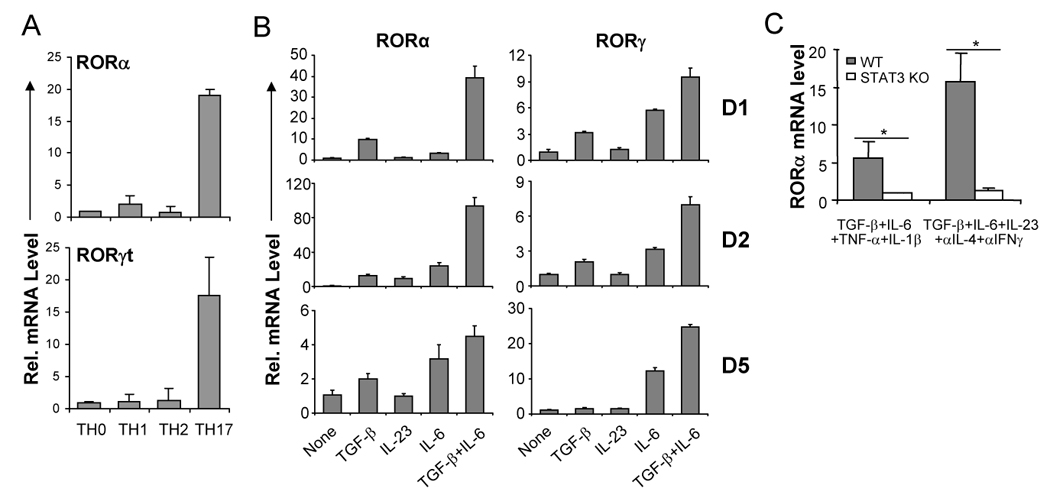
(A) CD4+ T cells from OTII mice were differentiated with OVA323–339 peptide and splenic antigen presenting cells (APCs) under neutral (TH0), TH1, TH2 and TH17 conditions for 5 days, and RORα and RORγt mRNA expression levels were assessed by real-time RT-PCR after restimulation of T cells by anti-CD3 for 4 hours. Data shown are derived from 2 independent experiments with consistent results and normalized using expression levels of Actb. Expression levels in TH0 were referred as 1. (B) FACS-sorted naïve CD4+CD25−CD62LhiCD44lo T cells from C57BL/6 mice were activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence of indicated cytokine stimuli for 1, 2 or 5 days, and RORα and RORγ mRNA expression levels were assessed by real-time RT-PCR. Expression levels in the condition without exogenous cytokine stimulus were referred as 1. (C) Naïve CD4+ T cells from STAT3 KO or wild-type (WT) mice were activated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 under the indicated stimuli for 4–5 days. RORα mRNA expression levels were assessed by real-time RTPCR. The expression levels in STAT3 KO cells were referred as 1. The experiments were repeated at least 3 times with consistent results. *, student t test p≤0.05.
