Figure 3. Close views of the base-flipping regions.
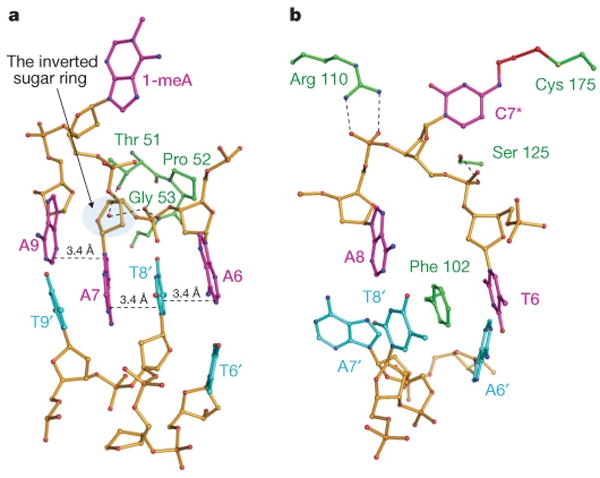
a, AlkB–DNA4 complex, with the same colouring as in Fig. 1b. A7 stacks with the A9:T9′ base pair. Thr 51 and Gly 53 are hydrogen bonded to the phosphate linking A7 and A6 (Supplementary Fig. 10b). The sugar ring of A9 adopts the 3′-endo conformation whereas the sugar ring of A7 is forced to be inverted by about 180° by the protein. T8′ from the complementary strand intercalates between A7 and A6, forming a one-base-wide stack containing bases from both strands. b, ABH2–DNA2 complex, with the same colour coding as in Fig. 1b. Phe 102 inserts into the DNA duplex with A7′ as the orphaned base.
