FIG. 1.
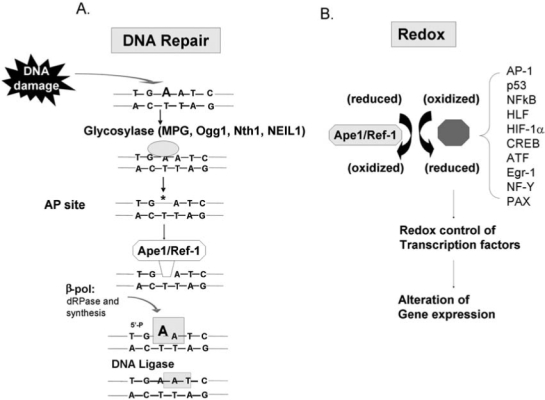
Oxidative and alkylation DNA damage is effectively repaired by the DNA BER pathway. This is a very simplified drawing of the DNA BER pathway. For a more detailed discussion, see Fishel et al. (21). (A) Damaged bases (in this case an N3-adenine) are removed by glycosylases that result in baseless or apurinic (AP) sites. Ape1 acts on AP sites, produces a nick that allows É-polymerase to insert the correct base and DNA ligase to connect the DNA backbone. (B) In addition to its repair function, Ape1 also serves as a redox factor maintaining transcription factors in an active reduced state. Some example targets are shown. Therefore, the protection of Ape1 from DNA damage may be twofold: directly through its DNA-repair function and indirectly through its redox activity by enabling transcription factors to bind to DNA and respond to the DNA damage. Lack of Ape1 activity may lead to cell death.
