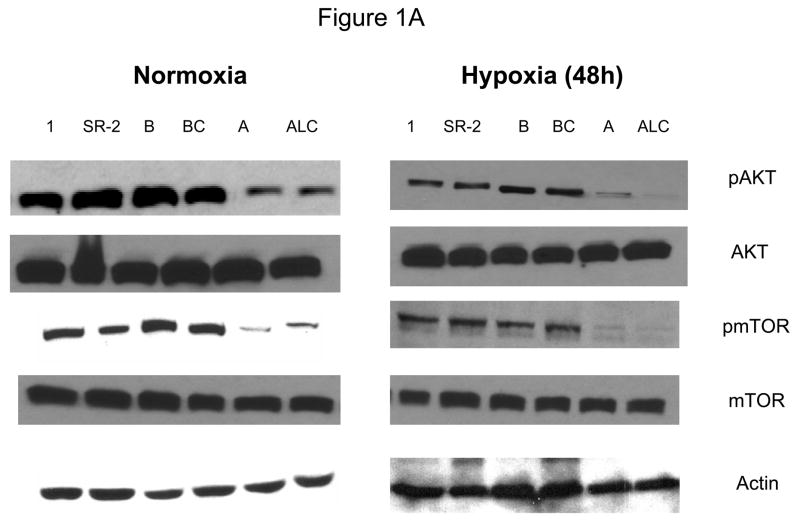
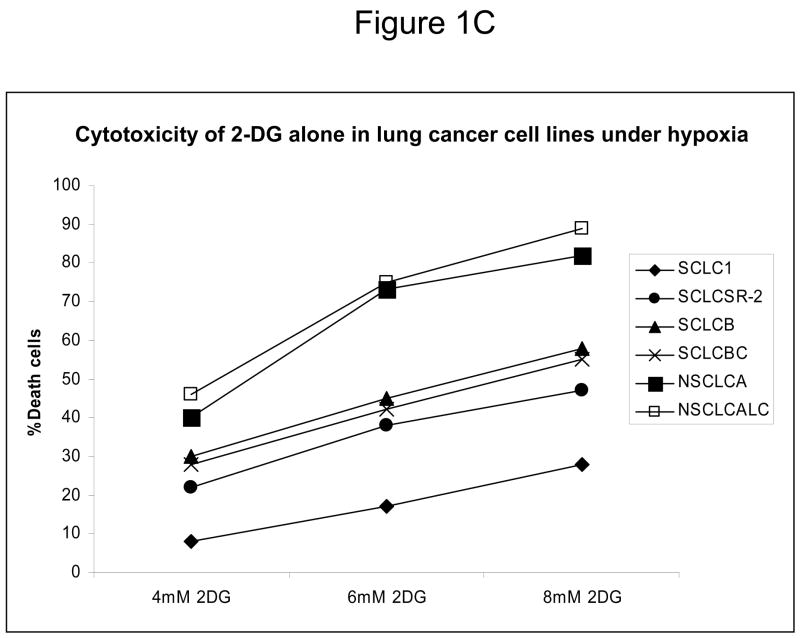
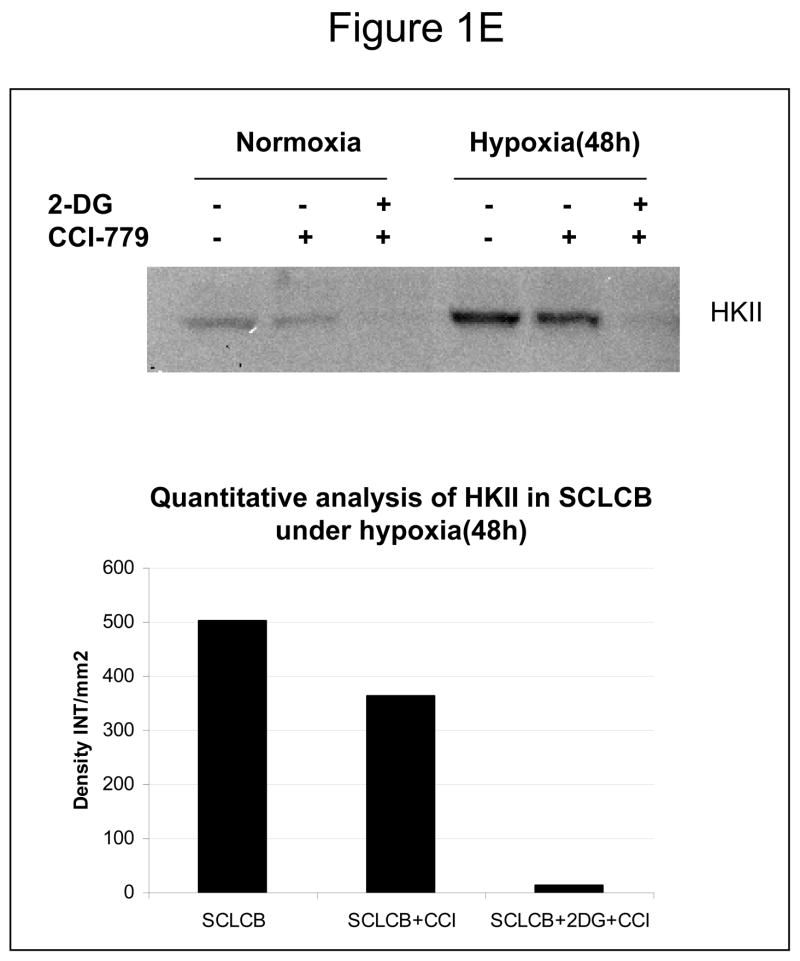
Figure 1.
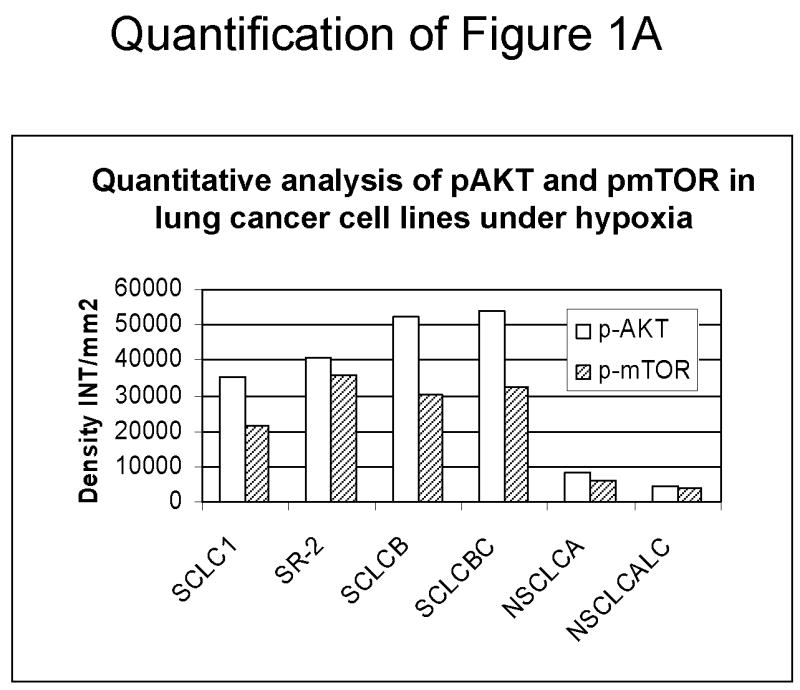
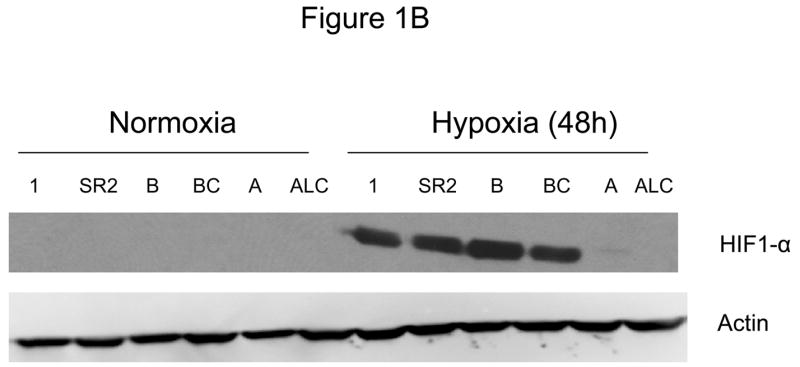
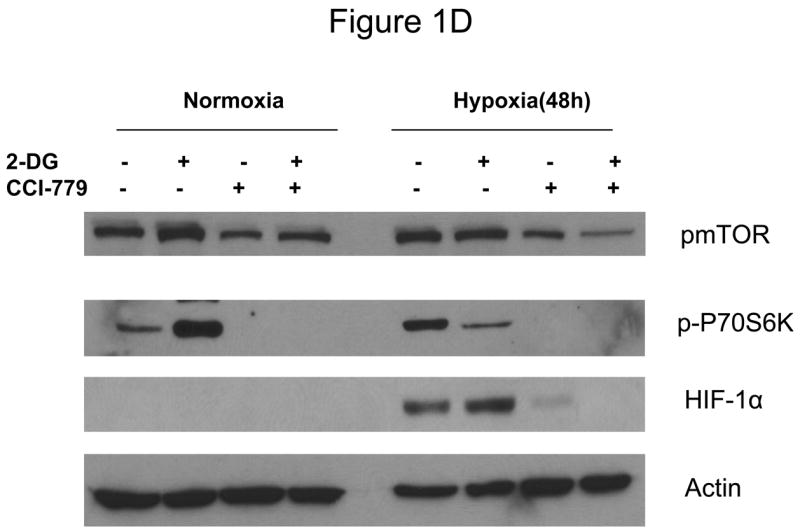
Decreased AKT and mTOR activity in lung cancer cell lines correlates with reduced levels of HIF-1α and increased sensitivity to 2-DG under hypoxia. (A) Western blots and quantitative analysis of pAKT and pmTOR levels in lung cancer cell lines grown under normoxia or hypoxia for 48hrs. Under normoxia as well as hypoxia, 2 NSCLC lines displayed intrinsically low levels of pAKT and pmTOR as compared to 4 SCLC lines. (B) Immunoblots of cells grown under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 48hr showed increased HIF-1α in those cell lines with expressing high levels of pAKT and pmTOR (SCLC lines) whereas in the NSCLC lines which expressed lower levels of pAKT and pmTOR, HIF-1α was barely detectable. (C) Low levels of HIF-1α in NSCLC lines correlated with increased sensitivity to 2-DG under hypoxia (48h). Each data point is the average of triplicate samples with S. D.; P<0.05. (D) Immunoblots of pmTOR, p-P70S6K, and HIF-1α in SCLC line B treated with 4mM of 2-DG or 0.1μg/ml of CCI-779 alone and in-combination under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions for 48hr. Note that under hypoxic conditions, CCI-779 down-regulates HIF-1α and when 2-DG is added, HIF-1α is completely eliminated. (E) Immunoblot of HKII expression in SCLC line B when treated with 0.1μg/ml of CCI-779 alone or in combination with 4mM of 2-DG under 48h of normoxia and hypoxia. Quantitative analysis indicates that HKII is decreased by 30% when SCLC line B under hypoxia is treated with CCI-779 alone and further reduced when co-treated with 2-DG (4mM).