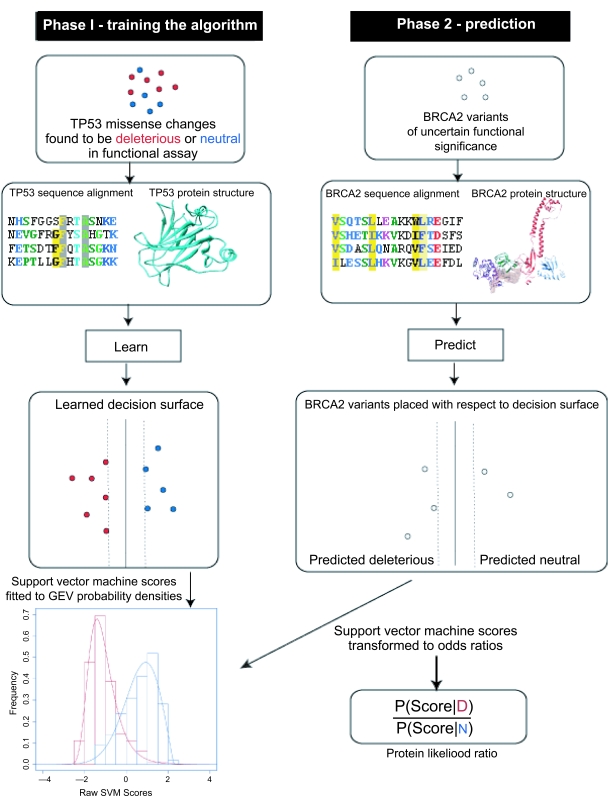
Figure 1.
Protein likelihood ratio algorithm. In the first phase, a support vector machine learns a decision surface that separates deleterious (red) and (blue) neutral missense changes in TP53, based on predictive properties from protein sequence and structure. The discriminant scores of TP53 missense changes are fit to a mixture of Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) probability densities (Red = deleterious scores, Blue = neutral scores). In the second phase, a BRCA2 missense variant is classified as deleterious or neutral using equivalent predictive properties. The discriminant score is transformed into a likelihood ratio that quantifies the odds that the score reflects a deleterious (D) or neutral (N) missense variant.