Figure 6. Ca2+/CaM regulates hVps34 lipid kinase activity.
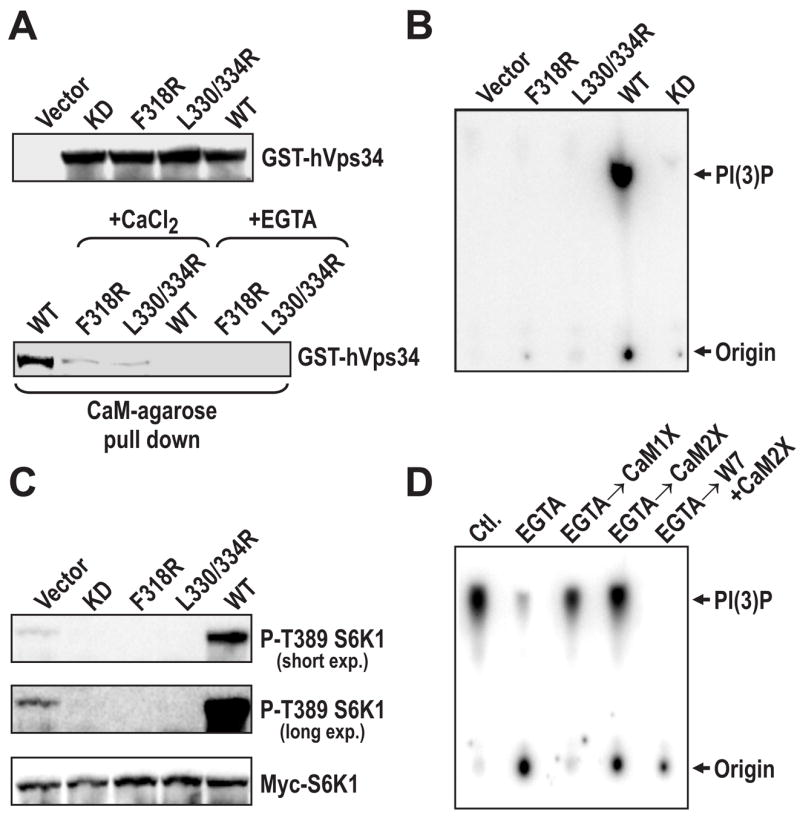
(A) HEK 293 cells were transfected with vectors expressing WT or CaM-binding mutants of hVps34 (Experimental Procedures). Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cells were treated as in Figure 1A, then cell lysates were prepared and used to measure the expression levels of each construct (upper panel) or for Ca2+/CaM-binding assays (lower panel), as in Figure 4C. (B) Equal amounts of WT, KD, and CaM-binding mutants of hVps34 expressed in HEK 293 cells, treated with AAs (Figure 6A), were immunoprecipitated with an anti-GST antibody and lipid kinase assays were performed on the immune complex in the presence of 0.5 mM CaCl2, as previously described (Nobukuni et al., 2005). (C) HEK 293 cells were transfected with either with WT, KD or the CaM-binding hVps34 mutants with myc-S6K1, treated with AAs as in Figure 1A, then cell lysates were prepared and probed with indicated antibodies. (D) HEK 293 cells were treated with AAs as in Figure 1A, endogenous hVps34 was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts in the presence of 0.5 mM CaCl2 or 2 mM EGTA. The resulting hVps34 immunoprecipitate was then extensively washed in either 0.5 mM CaCl2 or 2 mM EGTA, as in Supplemental Data, Figure S4C. The hVps34 immunoprecipitates were either directly assayed for lipid kinase activity as in Figure 3D or after the indicated additions (Experimental Procedures), as previously described (Nobukuni et al., 2005).
