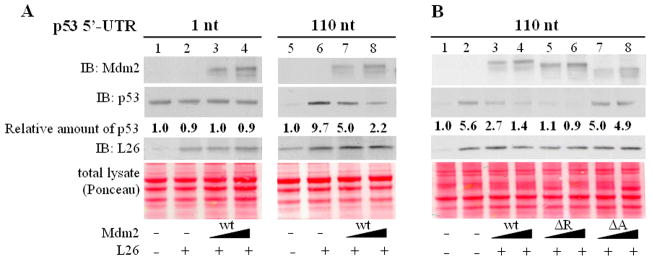
Figure 6. Mdm2 inhibits L26-mediated enhancement of p53 translation in vitro.
PCR products consisting of a T7 promoter-tagged p53 cDNA harboring a 1nt or 110nt 5′UTR, L26 cDNA and human Mdm2 cDNA (wild type (wt), RING domain deletion (ΔR), acidic domain deletion (ΔA)) were in vitro transcribed/translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysates in the presence of [35S] methionine. Reticulocyte lysates were pre-treated with 50μM MG132 for 15 minutes at room temperature prior to the addition of PCR-generated cDNAs. Lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
A. Effect of L26 on translation of p53 mRNA harboring a 1 or 110nt 5′UTR in the absence or presence of increasing wtMdm2 (1:1 and 1:2 ratio of L26 cDNA to Mdm2 cDNA). Amounts of total L26, including the endogenous L26 of the reticulocyte lysate, is shown in the middle panel. Equal loading was assessed by Ponceau staining of the membrane (bottom panel).
B. Effect of L26 on translation of p53 mRNA harboring a 110nt 5′UTR in the absence or presence of increasing Mdm2 (wild-type, ΔR, ΔA). Analysis was as in A.