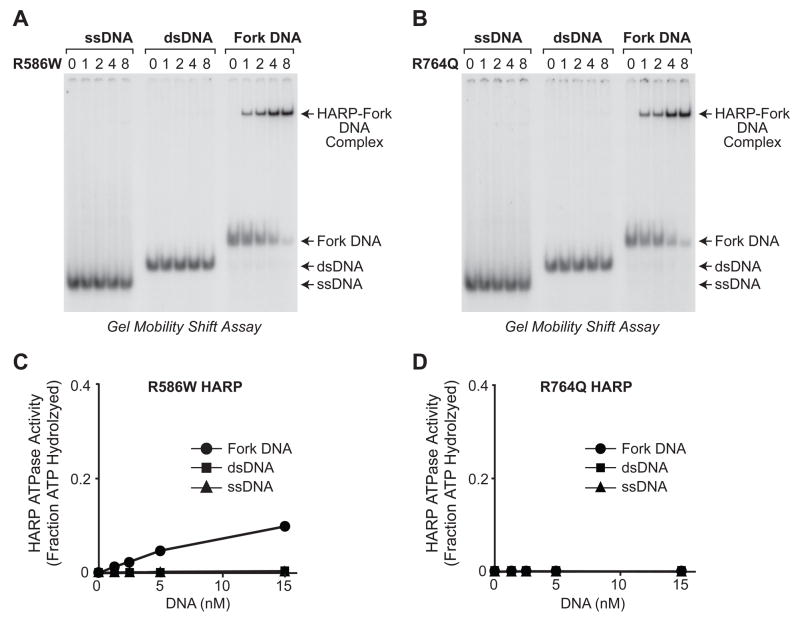
Fig. 3.
Mutant HARP proteins bind selectively to fork DNA, but exhibit less ATPase activity than wild-type HARP. The R764Q mutation results in a stronger SIOD phenotype than the R586W mutation (5). (A, B) The mutant HARP proteins bind with higher affinity to fork DNA than to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). These gel mobility shift experiments were performed as in Fig. 1A. (C, D) The R586W HARP protein has low ATPase activity, whereas the R764Q HARP protein has no detectable ATPase activity. ATPase assays were carried out as in Fig. 1B. Error bars represent SD (N = 3).