Figure 1.
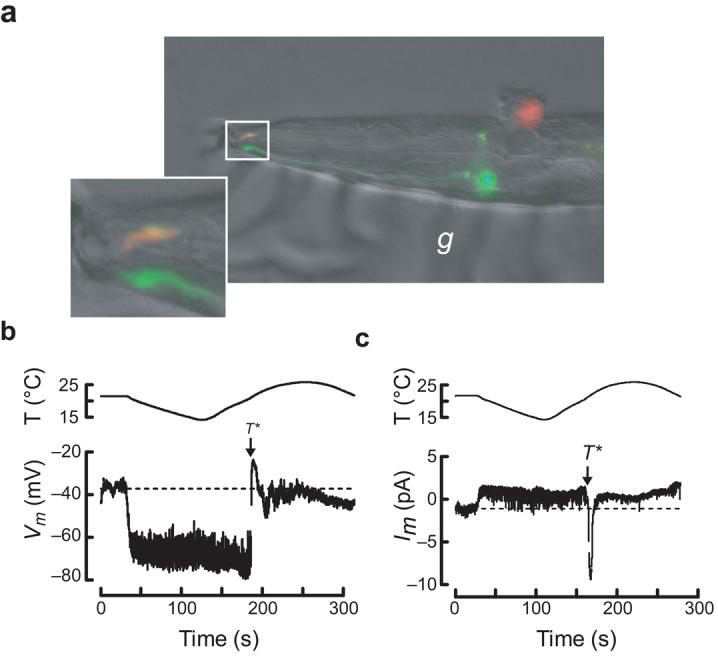
in vivo recording from wild-type C. elegans thermosensory neurons. (a) Micrograph of a dissected AFD neuron following whole-cell patch-clamp recording. The top (red), but not the bottom (green), AFD neuron was labeled by sulforhodamine 101 delivered by the recording pipette. The inset shows the worm's nose and labeled sensory endings of both AFD neurons. The micrograph is a dual-color fluorescence image digitally overlaid on a differential interference constrast (DIC) image of the same preparation. Anterior is to the left. g, glue used to immobilize the worm. (b) AFD receptor potential in response to a thermal ramp. (c) AFD receptor current in response to a thermal ramp (Vh = −60 mV). Data acquisition was interrupted periodically to reprogram the temperature controller (indicated by gaps in the traces).
