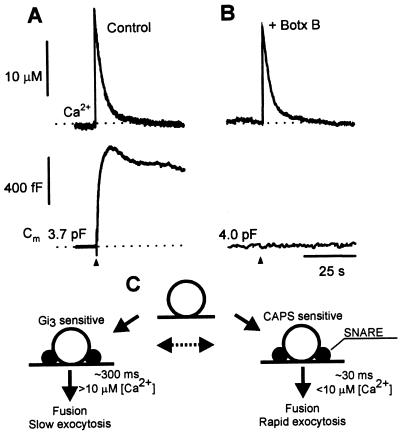
Figure 6.
Botulinum toxin B pretreatment inhibits changes in Cm. Time-dependent changes in [Ca2+]i (Upper) and Cm (Lower) in (A) a control cell and (B) in a cell pretreated by botulinum neurotoxin B (+ Botx B). Note the complete absence in a rise in Cm after the flash-induced rise in [Ca2+]i (Upper). Dotted lines indicate resting [Ca2+]i and Cm. (C) Model describing CAPS- and Gαi3-antibody action (25) on kinetic components of Cm. Vesicles entering rapid and slow exocytosis are recruited from a common pool that appears to be closely associated with the plasmamembrane (25). From this pool vesicles exocytose along biochemically distinct mechanisms. Typical reaction time constants and threshold [Ca2+]i for the CAPS-antibody- and Gαi3-antibody-sensitive pathways are indicated near the arrows. Endocytosis is not depicted but is assumed to proceed for each type of exocytosis separately. The possibility that the two functional states of exocytosis can be interconverted is indicated by the broken arrow.