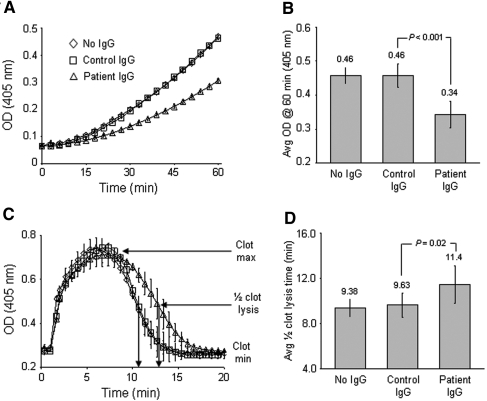
Figure 3.
Functional effects of antiplasminogen antibodies. (A) An in vitro assay was performed to determine the rate of plasmin formation in the presence of antiplasminogen antibodies by combining plasminogen, uPA or tPA, and a chromogenic substrate with and without control human IgG or affinity-purified antibodies. Shown is the average of two replicates for one patient's antibodies in the presence of uPA. (B) The average ± SD absorbance after 60 min is shown from two independent experiments for patients A and B with both uPA and tPA. Antiplasminogen antibodies decreased the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, when compared with HBS buffer or normal human IgG at the same concentration. (C) An in vitro clotting assay examined how antiplasminogen antibodies affect fibrin clot formation and/or dissolution. Normal human plasma was combined with HBS buffer alone, normal human IgG, or patient antiplasminogen antibodies, in the presence of thrombin and uPA. Clot formation and dissolution were monitored by change in absorbance at 405 nm. Shown is the average ± SD of two replicates for one patient's antibodies. (D) The average ± SD ½ clot lysis time is shown from two independent experiments for patients A and B. Antiplasminogen antibodies delayed the fibrinolysis of the clot. Statistical analysis done by t test.