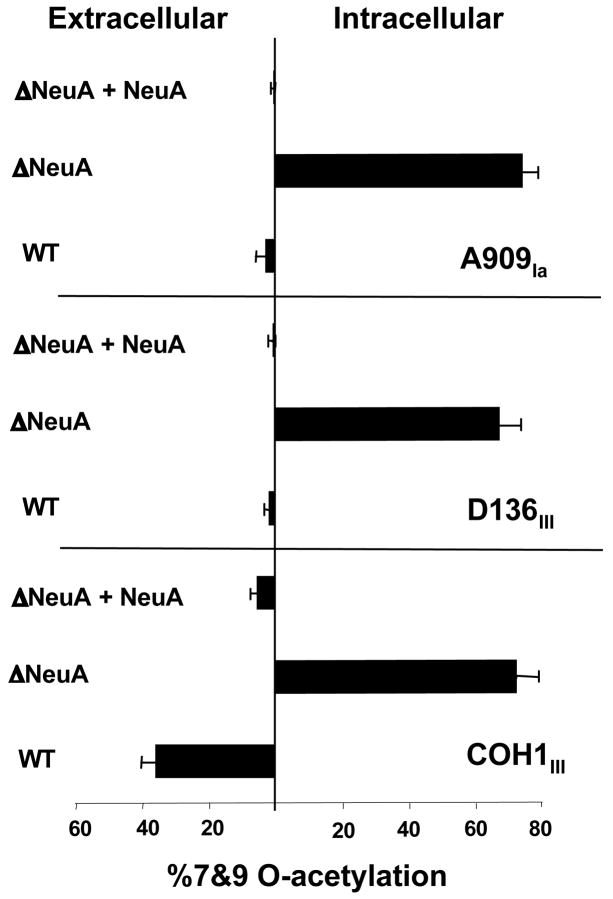
Figure 6. Deletion of GBS NeuA increases intracellular Sia-O-acetylation in both “high-OAc” and “low-OAc” strains.
Elimination of NeuA (both CMP-Sia synthestase and esterase domains) in different GBS strains was accomplished by precise allelic replacement of the neuA gene with chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cat) to produce the ΔNeuA or “ΔA” strains as described in Experimental Procedures. Mutant strains were complemented by plasmid-based expression of NeuA (“+A”) as in Figure 4. Intracellular and extracellular Sias were separated as previously described (17) and percent O-acetylation was determined by DMB-HPLC analysis. HPLC profiles of the wild-type COH1 and corresponding ΔNeuA strain were published previously (17). Bars represent standard deviation of 2 or more independent experiments.