Figure 6. Inhibition of RASMC proliferation and migration by EA.
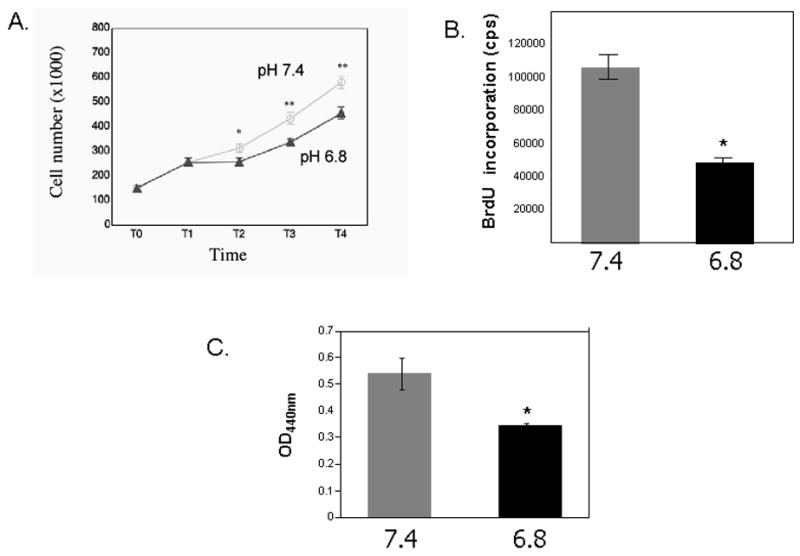
A. Cell number in response to serum and Platelet-derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB). Quadruplicate cultures of primary rat VSMCs were plated at equal numbers and grown to 40% confluence (T0). They were serum deprived (0.5% FBS) for 48 hours (T1) and then stimulated to proliferate in serum in media of pH 6.8 or pH 7.4 overnight (T2). A second growth stimulus (PDGF-BB, 25ng/ml) was then added and cell counts were assessed 18 hours (T3) and 48 hours (T4) after the addition of PDGF-BB. The mean and SEM values are shown * p< 0.05, ** p<0.001(comparisons were made between the two experimental conditions). B. BrdU incorporation in primary RASMCs in response to PDGF-BB in the setting of extracellular acidosis (pH6.8) or physiologic pH (7.4). RASMCs were plated at equal numbers (15,000 cells/well in a 96-well plate) and incubated at 37° C overnight to ensure attachment. Plating efficiency was assessed by counting cell numbers in parallel cultures 24 hours later. Cells were serum deprived for 48 hours then stimulated to proliferate with PDGF-BB (25ng/ml) in media of pH 6.8 or pH 7.4 overnight. A 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) chemiluminescence immunoassay (Roche) was used to measure DNA synthesis. Mean and SEM are shown. *p<0.0001. C. Cell migration assays were performed using Transwell plates (Transwell-Costar corp). Subconfluent cells of primary RASMCs were trypsinized, neutralized and resuspended in DMEM, 0.1% BSA. The same number of cells (5×105) were added to the top of each migration chamber in the setting of extracellular acidosis (pH 6.8) or physiologic pH (7.4) and were allowed to migrate to the underside of the chamber overnight in the presence of 50ng/ml PDGF-BB in the lower chamber. The upper side of the filter was then scraped off and the filter was removed. VSMC that had migrated to the lower side of the filter were quantified with an acid phosphatase enzymatic assay. Mean optical density at 440nm (OD440nm) and SEM are shown* p<0.05
