Fig. 6. PARP-1 -related events in response to ethanol exposure.
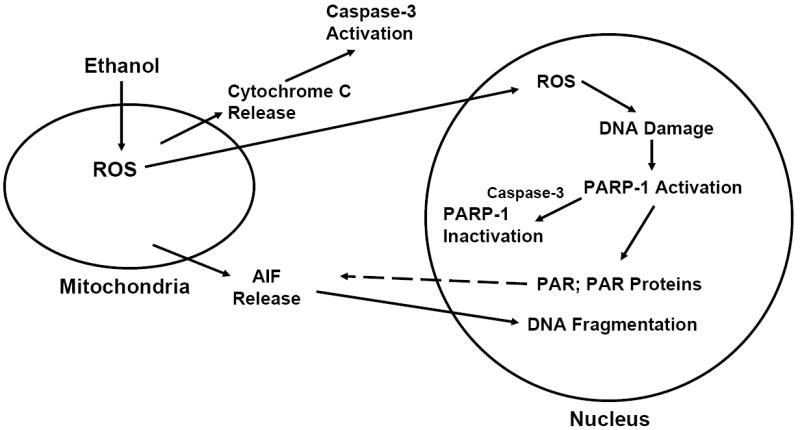
Within minutes of ethanol exposure, there is an enhanced expression of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cultured fetal rat cerebral cortical neurons (Heaton et al., 2003; Kotch et al., 1995; Maffi et al., 2008; Ramachandran et al., 2001, 2003). This scheme presents the concept that PARP-1 is activated secondary to DNA damage, ultimately leading to PARylation of nuclear proteins. Within 2 hours of ethanol exposure there is an observable increase in translocation of AIF to the nuclear compartment, an event that may be mediated by PARP-1. Within 12 hours of ethanol treatment, there is caspase-3 -mediated inactivation of PARP-1. However, the DNA fragmentation process has already commenced in select neurons, in response to nuclear accumulation of AIF.
