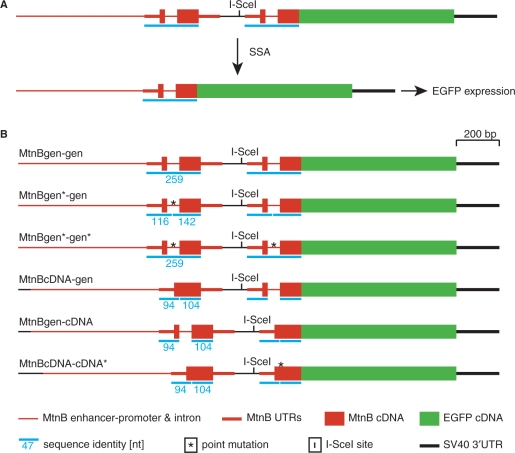
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of DNA constructs for SSA detection. (A) One of the two direct repeats, the one upstream of the I-SceI endonuclease cleavage site, is under the control of the mtnB enhancer/promoter. The coding region of the downstream repeat, lacking regulatory sequences for transcription, is fused in-frame to the EGFP cDNA. Induction of transcription does not lead to expression of EGFP protein, unless the DSB, generated by the endonuclease I-SceI, is repaired via SSA of the flanking metallothionein copies. (B) All constructs contain an I-SceI endonuclease recognition site (I-SceI), which is flanked by genomic (gen) or cDNA copies of mtnB. The length of sequence identity between tandem duplicates is indicated by blue bars and numbers, which represent nucleotide numbers. The longest stretch of sequence identity is 259 nt in the construct containing two genomic mtnB copies (MtnBgen-gen). This identity is disturbed in several constructs either by a silent point mutation (MtnBgen*-gen, MtnBcDNA-cDNA*) or the absence of the intron (MtnBcDNA-gen, MtnBgen-cDNA).