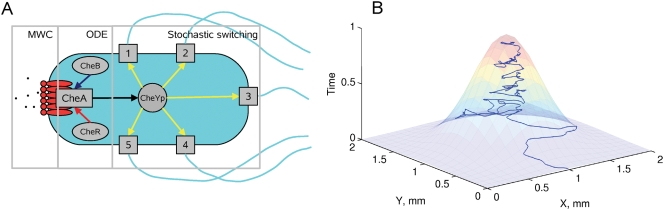
Figure 1. Model of chemotactic E. coli.
(A) Scheme of the hybrid model. The activity of the receptor cluster depends on the local ligand concentration and the methylation level according to the MWC model. Methylation (red arrow) and demethylation (blue arrow) are performed by CheR and CheB. The phosphate group is transferred from active CheA to the response regulator CheY (black arrow). The concentration of CheY-P modulates the motor bias of 5 independent motors (yellow arrows), and their collective behavior makes the cell run or tumble. Ligand binding, receptors cluster switching, CheY phosphorylation and motor switching are considered to be in rapid equilibrium and are described by algebraic equations, while the methylation and demethylation kinetics are relatively slow and simulated using an ODE. Motor switching is simulated stochastically. (B) The model reproduces the swimming of E. coli cells up gradients of attractants, taking into account the effect of rotational diffusion. A typical path of a swimming virtual cell is shown in 2D space, with the relative time course shown along the Z axis, demonstrating how the cell finds the maximum attractant concentration and stays in its vicinity. The attractant concentration profile is overlayed.