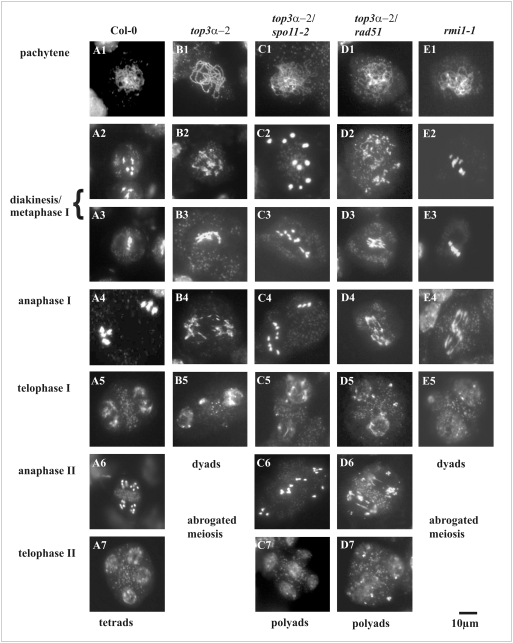
Figure 5. DAPI staining of different meiotic stages during pollen development in the mutant lines.
Wild type meiosis (A1–7) is characterized by synapsis of homologous chromosomes and the formation of bivalents during the pachytene stage of prophase (A1). During diakinesis, the chromosome pairs condensed for the first meiotic division (A2). At metaphase I, homologues assembled at the metaphase plate (A3). During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separated to the poles (A4) and decondensed in telophase I (A5). During anaphase II, the chromatids slightly condensed and separated (A6), followed by another decondensation phase in telophase II and ended up in tetrads (A7). The mutant lines top3α-2 and rmi1-1 both exhibited chromosome fragmentation became visible in diakinesis and ending in telophase I (B2 to B5 and E2 to E5). Furthermore, both lines did not progress to meiosis II and showed an arrest in telophase I (B5 and E5). In the rmi1-1 mutants, massive amounts of stainable DNA fragments appeared stuck at the metaphase plate (compare B4 to E4). Double mutants of top3α-2 and two genes involved in early steps of meiotic DSB repair (Atspo11-2 and Atrad51) showed the respective phenotype of the background mutant in both cases, indicating that top3α-2 is involved in the latter steps of DSB repair (C1 to 7 and D1 to 7). The arrest in telophase I was released in spo11-2 or rad51 backgrounds, respectively.