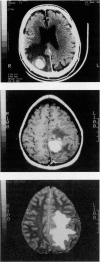
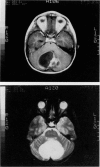
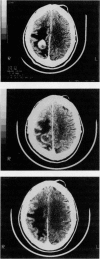
Abstract
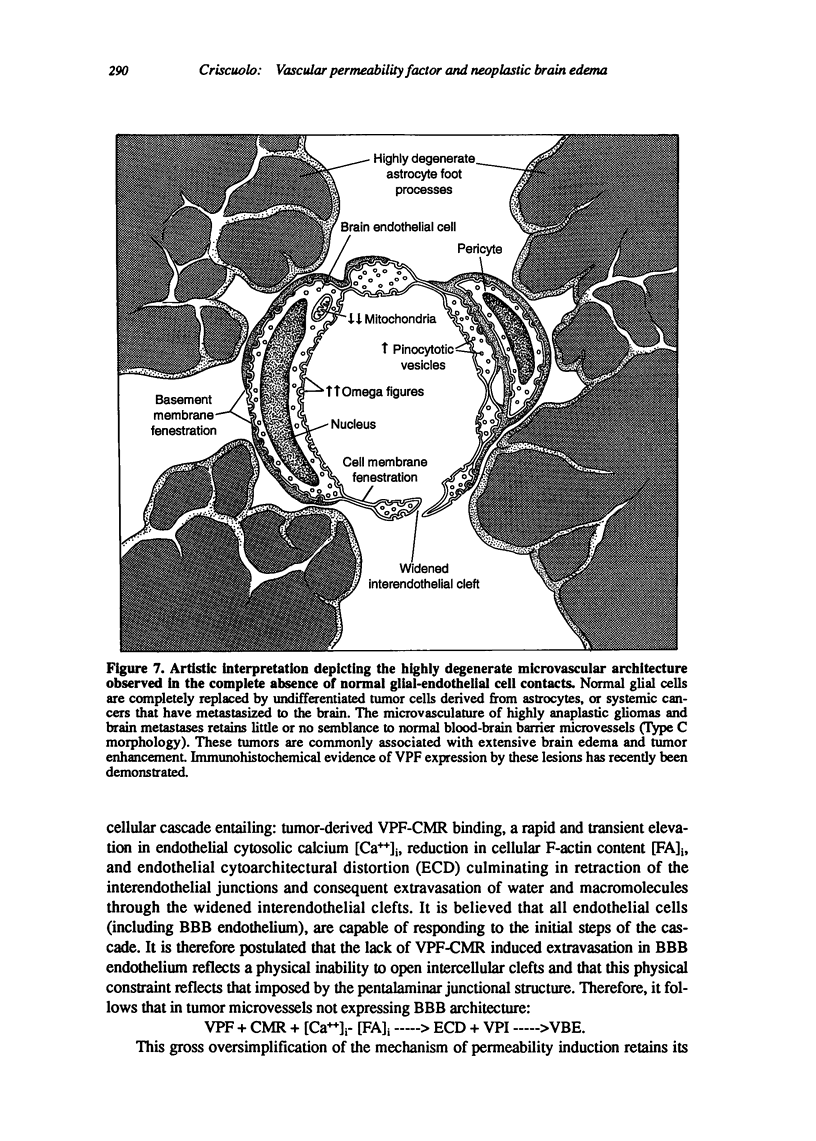
Cerebral edema and fluid-filled cysts are common accompaniments of brain tumors. They contribute to the mass effect imposed by the primary tumor and are often responsible for a patient's signs and symptoms. Cerebral edema significantly increases the morbidity associated with tumor biopsy, excision, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Both edema and cyst formation are thought to result from a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier, with consequent extravasation of water, electrolytes, and plasma proteins from altered tumor microvessels. The resultant expansion of the cerebral interstitial space contributes to the elevated intracranial pressure observed with brain tumors. Departure from the typical blood-brain barrier microvascular architecture may only partially explain the occurrence of edema and tumor cyst formation. Biochemical mediators have also been implicated in vascular extravasation. Vascular permeability factor or vascular endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF) is a protein that has recently been isolated from a variety of tumors including human brain tumors. VPFb is an extraordinarily potent inducer of both microvascular extravasation (edemagenesis) and the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Its role in tumor growth and progression would therefore appear pivotal. Herein, the author presents an updated account of the investigation of VPF. Historical and clinical perspectives of the study and treatment of tumor associated edema are provided. The efficacy of high-dose dexamethasone in the treatment of neoplastic brain edema is discussed. A hypothetical role for VPF in edemagenesis is presented and discussed. It is hoped that an expanded understanding of the mechanisms responsible for the genesis of edema will ultimately facilitate therapeutic intervention.
Full text
PDF






























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman N. B., Hechmer P. A. Studies on the capillary permeability of experimental liver metastases. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978 Jun;146(6):884–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alessandri G., Raju K. S., Gullino P. M. Interaction of gangliosides with fibronectin in the mobilization of capillary endothelium. Possible influence on the growth of metastasis. Invasion Metastasis. 1986;6(3):145–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammirati M., Galicich J. H., Arbit E., Liao Y. Reoperation in the treatment of recurrent intracranial malignant gliomas. Neurosurgery. 1987 Nov;21(5):607–614. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198711000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. L., Goldstein G. W. Transport of hexoses, potassium and neutral amino acids into capillaries isolated from bovine retina. Exp Eye Res. 1980 May;30(5):593–605. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(80)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black K. L., Hoff J. T. Leukotrienes increase blood-brain barrier permeability following intraparenchymal injections in rats. Ann Neurol. 1985 Sep;18(3):349–351. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman P. D., Betz A. L., Ar D., Wolinsky J. S., Penney J. B., Shivers R. R., Goldstein G. W. Primary culture of capillary endothelium from rat brain. In Vitro. 1981 Apr;17(4):353–362. doi: 10.1007/BF02618147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Klatzo I., Olsson Y., Reese T. S. The blood-brain barrier to proteins under normal and pathological conditions. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Mar;10(3):215–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Reese T. S. Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):648–677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Capasso E. A. Thrombin and histamine activate phospholipase C in human endothelial cells via a phorbol ester-sensitive pathway. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Jul;136(1):54–62. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J. N., Criscuolo G. R., Merrill M. J., Moquin R. R., Blacklock J. B., Oldfield E. H. Vascular permeability induced by protein product of malignant brain tumors: inhibition by dexamethasone. J Neurosurg. 1987 Dec;67(6):880–884. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.6.0880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M. F. Vasogenic edema with intraparenchymatous expanding mass lesions: a theory on its pathophysiology and mode of action of hyperventilation and corticosteroids. Med Hypotheses. 1984 Apr;13(4):439–450. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(84)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Fishman R. A. The role of arachidonic acid in vasogenic brain edema. Fed Proc. 1984 Feb;43(2):210–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claffey K. P., Wilkison W. O., Spiegelman B. M. Vascular endothelial growth factor. Regulation by cell differentiation and activated second messenger pathways. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16317–16322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Heuvelman D. M., Nelson R., Olander J. V., Eppley B. L., Delfino J. J., Siegel N. R., Leimgruber R. M., Feder J. Tumor vascular permeability factor stimulates endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1470–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI114322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Olander J. V., Heuvelman D., Nelson R., Monsell R., Siegel N., Haymore B. L., Leimgruber R., Feder J. Human vascular permeability factor. Isolation from U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20017–20024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criscuolo G. R., Lelkes P. I., Rotrosen D., Oldfield E. H. Cytosolic calcium changes in endothelial cells induced by a protein product of human gliomas containing vascular permeability factor activity. J Neurosurg. 1989 Dec;71(6):884–891. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.6.0884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criscuolo G. R., Merrill M. J., Oldfield E. H. Characterization of a protein product of human malignant glial tumors that induces microvascular permeability. Adv Neurol. 1990;52:469–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criscuolo G. R., Merrill M. J., Oldfield E. H. Further characterization of malignant glioma-derived vascular permeability factor. J Neurosurg. 1988 Aug;69(2):254–262. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.69.2.0254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Vaz J. G. The blood-retinal barriers. Doc Ophthalmol. 1976 Oct 15;41(2):287–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00146764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing H. I. Subtemporal Decompressive Operations for the Intracranial Complications Associated with Bursting Fractures of the Skull. Ann Surg. 1908 May;47(5):641–644.1. doi: 10.1097/00000658-190805000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey R. J., Roy M. W., Meyer K., Tai H. H., Olson J. W. Polyamine and prostaglandin markers in focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosurgery. 1985 Oct;17(4):635–640. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198510000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKEL S. A., GERMAN W. J. Glioblastoma multiforme; review of 219 cases with regard to natural history, pathology, diagnostic methods, and treatment. J Neurosurg. 1958 Sep;15(5):489–503. doi: 10.3171/jns.1958.15.5.0489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden A. I., Jacobs T. P., Patrick D. H., Smith M. T. Megadose corticosteroid therapy following experimental traumatic spinal injury. J Neurosurg. 1984 Apr;60(4):712–717. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.4.0712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell C. L., Shivers R. R. Capillary junctions of the rat are not affected by osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;63(3):179–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00685243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Henzel W. J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Houck K., Jakeman L., Leung D. W. Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):18–32. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Winer J., Henzel W. J. Purification and cloning of vascular endothelial growth factor secreted by pituitary folliculostellate cells. Methods Enzymol. 1991;198:391–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)98040-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkenzeller G., Marmé D., Weich H. A., Hug H. Platelet-derived growth factor-induced transcription of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene is mediated by protein kinase C. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 1;52(17):4821–4823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman R. A. Brain edema. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 2;293(14):706–711. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510022931407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Langer R., Linhardt R. J., Haudenschild C., Taylor S. Angiogenesis inhibition and tumor regression caused by heparin or a heparin fragment in the presence of cortisone. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):719–725. doi: 10.1126/science.6192498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALICICH J. H., FRENCH L. A. Use of dexamethasone in the treatment of cerebral edema resulting from brain tumors and brain surgery. Am Pract Dig Treat. 1961 Mar;12:169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. M., Savolaine E. R. Modification of tumor enhancement and brain edema in computerized tomography by corticosteroids: case report. Neurosurgery. 1980 Mar;6(3):282–284. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198003000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen M. E. Eicosanoid production by the coronary microvascular endothelium. Fed Proc. 1987 Jan;46(1):47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen M. E., Nganele D. M., Rodrigues A. M. Calcium ionophore (A23187)- and arachidonic acid-stimulated prostaglandin release from microvascular endothelial cells: effects of calcium antagonists and calmodulin inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):837–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitay-Goren H., Soker S., Vlodavsky I., Neufeld G. The binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its receptors is dependent on cell surface-associated heparin-like molecules. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6093–6098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick R. P., Molteni A., Fors E. M. Hormone binding in brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 1983 Nov;13(5):513–519. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198311000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A. Calcium channels and calcium channel antagonists. Ann Neurol. 1987 Apr;21(4):317–330. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudeman S. K., Miller J. D., Becker D. P. Failure of high-dose steroid therapy to influence intracranial pressure in patients with severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 1979 Sep;51(3):301–306. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.3.0301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Pearson J. D. Exogenous ATP raises cytoplasmic free calcium in fura-2 loaded piglet aortic endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harsh G. R., 4th, Levin V. A., Gutin P. H., Seager M., Silver P., Wilson C. B. Reoperation for recurrent glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. Neurosurgery. 1987 Nov;21(5):615–621. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198711000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatam A., Yu Z. Y., Bergström M., Berggren B. M., Greitz T. Effect of dexamethasone treatment on peritumoral brain edema: evaluation by computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1982 Jun;6(3):586–592. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198206000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Matsui T. Vascular structures in brain tumors. Hum Pathol. 1975 Sep;6(5):611–621. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(75)80045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi H., McKeehan W. L. Brain- and liver cell-derived factors are required for growth of human endothelial cells in serum-free culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6413–6417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossmann K. A., Hürter T., Oschlies U. The effect of dexamethasone on serum protein extravasation and edema development in experimental brain tumors of cat. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;60(3-4):223–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00691870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck K. A., Ferrara N., Winer J., Cachianes G., Li B., Leung D. W. The vascular endothelial growth factor family: identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1806–1814. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Anderson J. H., Long D. M. Oxygen free radicals in the genesis of traumatic and peritumoral brain edema. Neurosurgery. 1989 May;24(5):679–685. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198905000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Ikeda K., Long D. M. Comparative study of different iron-chelating agents in cold-induced brain edema. Neurosurgery. 1989 Jun;24(6):820–824. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198906000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilsen H. W., Sato M., Pawlik G., Herholz K., Wienhard K., Heiss W. D. (68Ga)-EDTA positron emission tomography in the diagnosis of brain tumors. Neuroradiology. 1984;26(5):393–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00327493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamura T., Nishio S., Takeshita I., Fujiwara S., Fukui M. Peritumoral brain edema in meningiomas--influence of vascular supply on its development. Neurosurgery. 1992 Aug;31(2):179–185. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199208000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito U., Reulen H. J., Tomita H., Ikeda J., Saito J., Maehara T. Formation and propagation of brain oedema fluid around human brain metastases. A CT Study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1988;90(1-2):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01541264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A. Endothelial cells and the biology of factor VIII. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 17;296(7):377–383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702172960707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakeman L. B., Winer J., Bennett G. L., Altar C. A., Ferrara N. Binding sites for vascular endothelial growth factor are localized on endothelial cells in adult rat tissues. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):244–253. doi: 10.1172/JCI115568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarden J. O., Dhawan V., Poltorak A., Posner J. B., Rottenberg D. A. Positron emission tomographic measurement of blood-to-brain and blood-to-tumor transport of 82Rb: the effect of dexamethasone and whole-brain radiation therapy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Dec;18(6):636–646. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOFMAN S., GARVIN J. S., NAGAMANI D., TAYLOR S. G., 3rd Treatment of cerebral metastases from breast carcinoma with prednisolone. J Am Med Assoc. 1957 Apr 20;163(16):1473–1476. doi: 10.1001/jama.1957.02970510039008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck P. J., Hauser S. D., Krivi G., Sanzo K., Warren T., Feder J., Connolly D. T. Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1309–1312. doi: 10.1126/science.2479987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzo I. Presidental address. Neuropathological aspects of brain edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jan;26(1):1–14. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196701000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblum J. A., Bay J. W., Gupta M. K. Steroid receptors in human brain and spinal cord tumors. Neurosurgery. 1988 Aug;23(2):185–188. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198808000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. K., Choi B., Sobel R. A., Chiocca E. A., Martuza R. L. Inhibition of growth and angiogenesis of human neurofibrosarcoma by heparin and hydrocortisone. J Neurosurg. 1990 Sep;73(3):429–435. doi: 10.3171/jns.1990.73.3.0429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohle P. N., Verhagen I. T., Teelken A. W., Blaauw E. H., Go K. G. The pathogenesis of cerebral gliomatous cysts. Neurosurgery. 1992 Feb;30(2):180–185. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199202000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D. M. Capillary ultrastructure and the blood-brain barrier in human malignant brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 1970 Feb;32(2):127–144. doi: 10.3171/jns.1970.32.2.0127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D. M. Capillary ultrastructure in human metastatic brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 1979 Jul;51(1):53–58. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.1.0053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D. M., Hartmann J. F., French L. A. The response of human cerebral edema to glucosteroid administration. An electron microscopic study. Neurology. 1966 May;16(5):521–528. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.5.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D. M. Vascular ultrastructure in human meningiomas and schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 1973 Apr;38(4):409–419. doi: 10.3171/jns.1973.38.4.0409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E. Studies on inflammation. 1. The effect of histamine and serotonin on vascular permeability: an electron microscopic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:571–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majno G., Gilmore V., Leventhal M. On the mechanism of vascular leakage caused by histaminetype mediators. A microscopic study in vivo. Circ Res. 1967 Dec;21(6):833–847. doi: 10.1161/01.res.21.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Milani D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Fura-2 measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in monolayers and suspensions of various types of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D. The management of cerebral oedema. Br J Hosp Med. 1979 Feb;21(2):152–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myoken Y., Kayada Y., Okamoto T., Kan M., Sato G. H., Sato J. D. Vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) produced by A-431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells and identification of VEGF membrane binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5819–5823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northover A. M., Northover B. J. Changes of vascular endothelial cell shape and of membrane potential in response to the ionophore A23187. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1987;6(2):137–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olander J. V., Connolly D. T., DeLarco J. E. Specific binding of vascular permeability factor to endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H., Cornford M. E., Brown W. J. The large apparent work capability of the blood-brain barrier: a study of the mitochondrial content of capillary endothelial cells in brain and other tissues of the rat. Ann Neurol. 1977 May;1(5):409–417. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A., Poy E., Woodward D. F., Daniel D. Evaluation of the role of Histamine H1- and H2-receptors in cutaneous inflammation in the guinea-pig produced by histamine and mast cell degranulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;69(4):615–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon J., Foncin J. F., Grob R., Srour A., Poisson M., Pertuiset B. F. Cerebral edema associated with meningiomas: possible role of a secretory-excretory phenomenon. Neurosurgery. 1984 Mar;14(3):295–301. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198403000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poungvarin N., Bhoopat W., Viriyavejakul A., Rodprasert P., Buranasiri P., Sukondhabhant S., Hensley M. J., Strom B. L. Effects of dexamethasone in primary supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 14;316(20):1229–1233. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705143162001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quindlen E. A., Bucher A. P. Correlation of tumor plasminogen activator with peritumoral cerebral edema. A CT and biochemical study. J Neurosurg. 1987 May;66(5):729–733. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.66.5.0729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman H. R., Farrell C. L., Del Maestro R. F. Effects of steroids and nonsteroid anti-inflammatory agents on vascular permeability in a rat glioma model. J Neurosurg. 1986 Aug;65(2):233–237. doi: 10.3171/jns.1986.65.2.0233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reulen H. J. Vasogenic brain oedema. New aspects in its formation, resolution and therapy. Br J Anaesth. 1976 Aug;48(8):741–752. doi: 10.1093/bja/48.8.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. A., Megyesi J. F., Henzel W. J., Ferrara N., Folkman J. Conditioned medium from mouse sarcoma 180 cells contains vascular endothelial growth factor. Growth Factors. 1990;4(1):53–59. doi: 10.3109/08977199009011010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I. Histamine type I receptor occupancy increases endothelial cytosolic calcium, reduces F-actin, and promotes albumin diffusion across cultured endothelial monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2379–2387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford R. B., Ross R. Platelet factors stimulate fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells quiescent in plasma serum to proliferate. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):196–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Clements E., Habliston D., Ryan J. W. Isolation and culture of pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Tissue Cell. 1978;10(3):535–554. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(16)30347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Mortara M., Whitaker C. Methods for microcarrier culture of bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells avoiding the use of enzymes. Tissue Cell. 1980;12(4):619–635. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(80)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler N., Knödgen B., Bartholeyns J. Polyamine metabolism and polyamine excretion in normal and tumor bearing rodents. Anticancer Res. 1985 Jul-Aug;5(4):371–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Connolly D. T., Van de Water L., Feder J., Dvorak H. F. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of guinea pig tumor-secreted vascular permeability factor. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 15;50(6):1774–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Perruzzi C. A., Harvey V. S., Dvorak H. F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Perruzzi C. A., Feder J., Dvorak H. F. A highly conserved vascular permeability factor secreted by a variety of human and rodent tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5629–5632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Sullivan J. M., Peach M. J. Role of endothelial cell cytoskeleton in control of endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 1982 Nov;51(5):657–661. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheline G. E. Radiation therapy of brain tumors. Cancer. 1977 Feb;39(2 Suppl):873–881. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197702)39:2+<873::aid-cncr2820390725>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N., Simionescu M., Palade G. E. Structural basis of permeability in sequential segments of the microvasculature of the diaphragm. II. Pathways followed by microperoxidase across the endothelium. Microvasc Res. 1978 Jan;15(1):17–36. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(78)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Werblowsky R. A permeability-enhancing factor produced by tumor. The genesis of malignant effusions. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1980;97(3):315–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00405784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbaugh L. J. Intracarotid infusions of protamine sulfate disrupt the blood-brain barrier of rabbits. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 21;409(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90705-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymaś J., Morkowski S., Tokarz F. Determination of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in human cerebrospinal fluid and in cyst fluid of brain tumors. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1986;83(3-4):144–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01402394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamiya Y., Friedlander R. M., Brem H., Malick A., Martuza R. L. Inhibition of angiogenesis and growth of human nerve-sheath tumors by AGM-1470. J Neurosurg. 1993 Mar;78(3):470–476. doi: 10.3171/jns.1993.78.3.0470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):307–312. doi: 10.1038/297307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. Mechanism of ionophore A23187 induction of plasma protein leakage and of its inhibition by indomethacin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 16;81(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer E., Mitchell R., Hartman T., Silva M., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C., Abraham J. A. The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11947–11954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J., Poenie M. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in individual small cells using fluorescence microscopy with dual excitation wavelengths. Cell Calcium. 1985 Apr;6(1-2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker W. S., Kirsch W. M., Martinez-Hernandez A., Fink L. M. In vitro plasminogen activator activity in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 1978 Feb;38(2):297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tósaki A., Koltai M., Joó F., Adám G., Szerdahelyi P., Leprán I., Takáts I., Szekeres L. Actinomycin D suppresses the protective effect of dexamethasone in rats affected by global cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1985 May-Jun;16(3):501–505. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueki H., Tsunemi S., Kubota Y. Vascular permeability-increasing action of hypoalbuminemic substance from Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. Gan. 1975 Jun;66(3):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood J. C., Carr I. The ultrastructure and permeability characteristics of the blood vessels of a transplantable rat sarcoma. J Pathol. 1972 Jul;107(3):157–166. doi: 10.1002/path.1711070303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterberg A., Baethmann A. J. The kallikrein-kinin system as mediator in vasogenic brain edema. Part 1: Cerebral exposure to bradykinin and plasma. J Neurosurg. 1984 Jul;61(1):87–96. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.61.1.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Hamilton J., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: modulation of enzyme production by anti-inflammatory steroids, mitotic inhibitors, and cyclic nucleotides. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehaskari V. M., Chang C. T., Stevens J. K., Robson A. M. The effects of polycations on vascular permeability in the rat. A proposed role for charge sites. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI111290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehaskari V. M., Root E. R., Germuth F. G., Jr, Robson A. M. Glomerular charge and urinary protein excretion: effects of systemic and intrarenal polycation infusion in the rat. Kidney Int. 1982 Aug;22(2):127–135. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyta J. C., Via D. P., Butterfield C. E., Zetter B. R. Identification and isolation of endothelial cells based on their increased uptake of acetylated-low density lipoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2034–2040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., PALADE G. E. NEW CYTOPLASMIC COMPONENTS IN ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:101–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Alexander E., Jr, Hunt W. E., MacCarty C. S., Mahaley M. S., Jr, Mealey J., Jr, Norrell H. A., Owens G., Ransohoff J., Wilson C. B. Evaluation of BCNU and/or radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic gliomas. A cooperative clinical trial. J Neurosurg. 1978 Sep;49(3):333–343. doi: 10.3171/jns.1978.49.3.0333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. T., Harker L. A., Quadracci L. J., Striker G. E. Factors influencing endothelial cell proliferation in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Aug;96(2):203–213. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040960209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. D., Hadfield M. G., Becker D. P., Lovings E. T. Endothelial fenestrations and other vascular alterations in primary melanoma of the central nervous system. Cancer. 1974 Dec;34(6):1982–1991. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197412)34:6<1982::aid-cncr2820340617>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weindel K., Marmé D., Weich H. A. AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma cells in culture express vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 31;183(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Bremer A. M., West C. R. Effects of dexamethasone on tumor-induced brain edema and its distribution in the brain of monkeys. J Neurosurg. 1979 Mar;50(3):361–367. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.50.3.0361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Ushio Y., Hayakawa T., Kato A., Yamada N., Mogami H. Quantitative autoradiographic measurements of blood-brain barrier permeability in the rat glioma model. J Neurosurg. 1982 Sep;57(3):394–398. doi: 10.3171/jns.1982.57.3.0394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Z. Y., Hatam A., Bergström M., Greitz T. CT findings and glucocorticoid receptors in intracranial lesions with edema. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Oct;5(5):619–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Z. Y., Wrange O., Boëthius J., Hatam A., Granholm L., Gustafsson J. A. A study of glucocorticoid receptors in intracranial tumors. J Neurosurg. 1981 Nov;55(5):757–760. doi: 10.3171/jns.1981.55.5.0757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziche M., Gullino P. M. Angiogenesis and neoplastic progression in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Aug;69(2):483–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries C., Escobedo J. A., Ueno H., Houck K., Ferrara N., Williams L. T. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):989–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1312256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]