Abstract
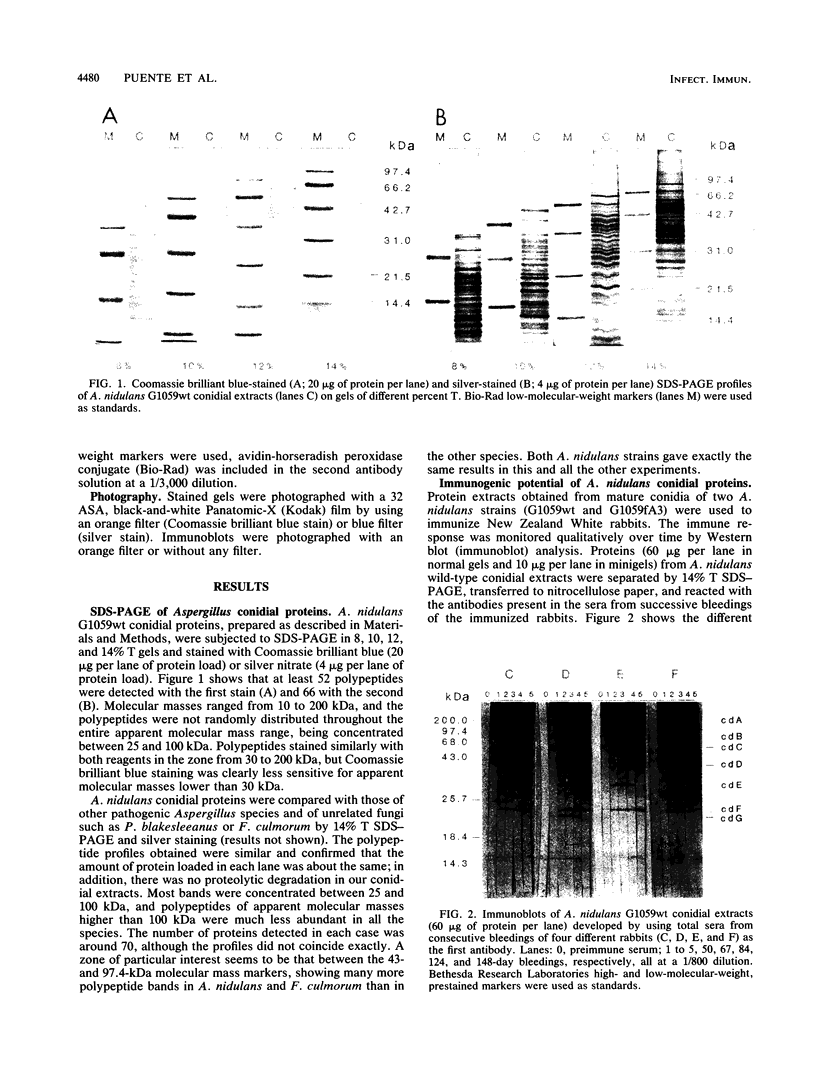
Aspergillus nidulans is an ascomycetous fungus that reproduces asexually by forming multicellular conidiophores and uninucleate spores called conidia. These elements constitute the main vehicle for the transmission of this and other pathogenic Aspergillus species and are the starting point of the different forms of aspergillosis. In order to use A. nidulans as a potential source of useful antigens for the immunodiagnosis of these diseases, we have examined the total protein composition of conidial extracts of this fungus by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in gels of different percent T. Injection of SDS-extracted conidial proteins into rabbits allowed us to raise a battery of polyclonal antibodies which have defined some important immunogenic polypeptides. Several of these immunogens were both present in mycelial extracts and recognized by antimycelium antibodies. Four of them, designated cdA, cdB, cdC, and cdE, were also found in conidial extracts of other pathogenic Aspergillus species. Only cdE was undetectable in cell extracts of the nonrelated species Fusarium culmorum and Phycomyces blakesleeanus.
Full text
PDF

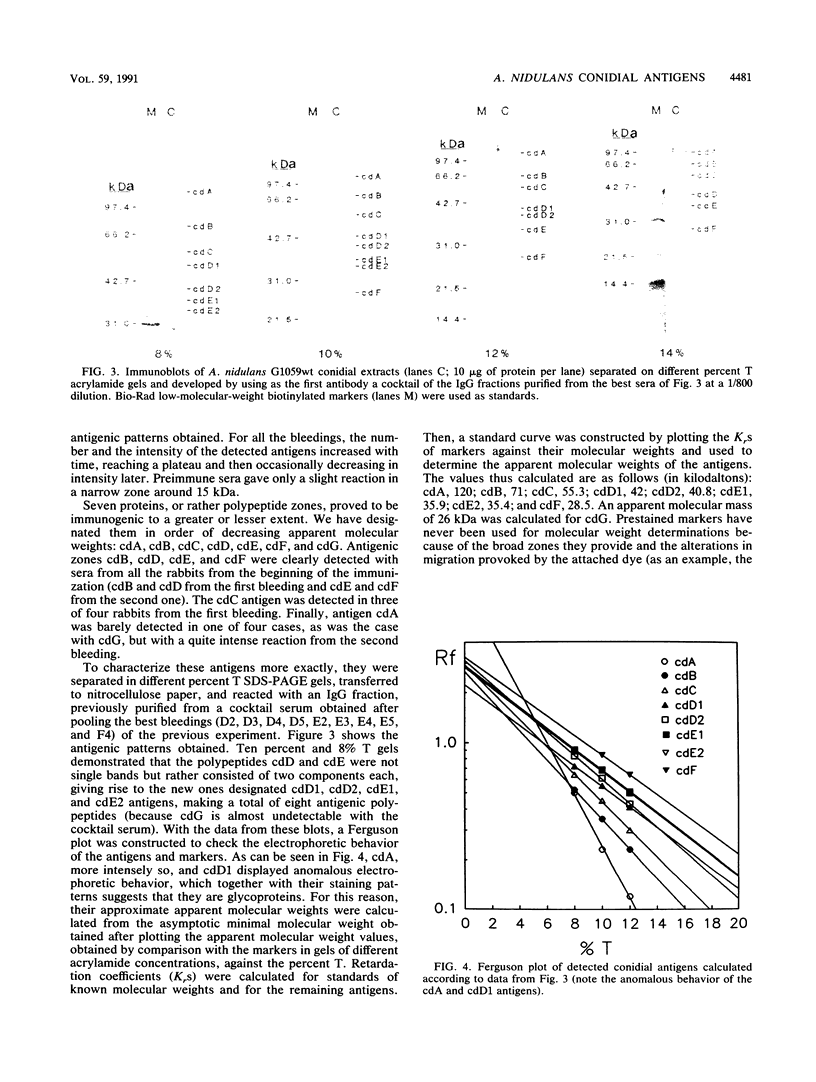

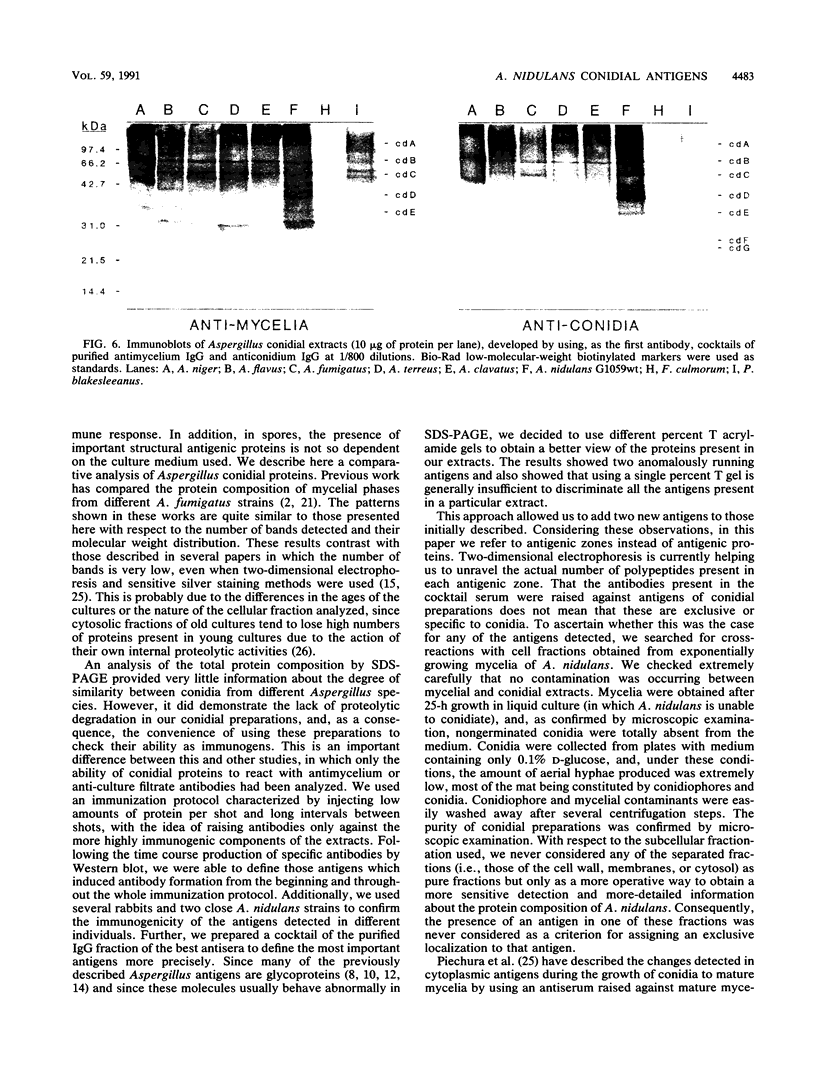
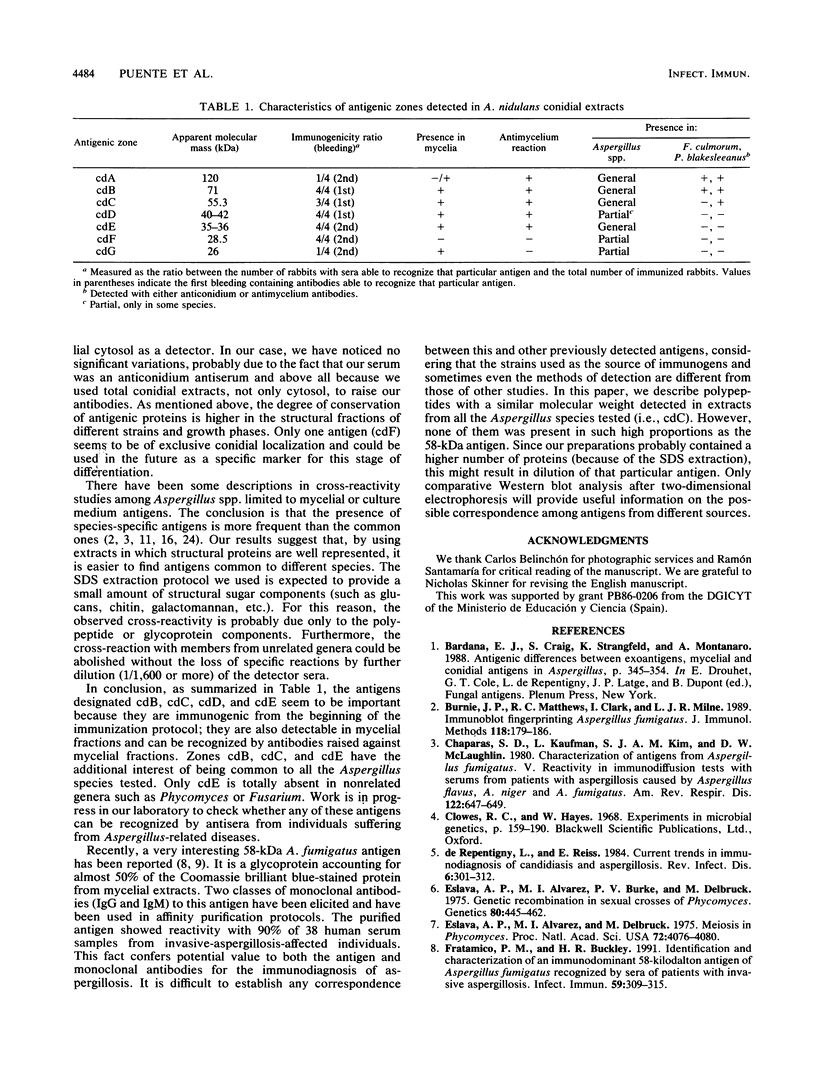

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnie J. P., Matthews R. C., Clark I., Milne L. J. Immunoblot fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Mar 31;118(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaparas S. T., Kaufman L., Kim S. J., McLaughlin D. W. Characterization of antigens from Aspergillus fumigatus. V. Reactivity in immunodiffusion tests with serums from patients with aspergillosis caused by Aspergillus flavus, A. niger, and A fumigatus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Oct;122(4):647–650. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eslava A. P., Alvarez M. I., Burke P. V., Delbrück M. Genetic recombination in sexual crosses of phycomyces. Genetics. 1975 Jul;80(3):445–462. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eslava A. P., Alvarez M. I., Delbrück M. Meiosis in Phycomyces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4076–4080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratamico P. M., Buckley H. R. Identification and characterization of an immunodominant 58-kilodalton antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus recognized by sera of patients with invasive aspergillosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.309-315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratamico P. M., Long W. K., Buckley H. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to a 58-kilodalton antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):316–322. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.316-322.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey C., Longbottom J. L. Characterization of a major antigenic component of Aspergillus fumigatus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):206–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman H. F., van der Heide S., Beaumont F., de Monchy J. G., de Vries K. The allergenic and antigenic properties of spore extracts of Aspergillus fumigatus: a comparative study of spore extracts with mycelium and culture filtrate extracts. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 May;73(5 Pt 1):567–573. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90512-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., John K. V., Resnick A., Fink J. N. A partially purified glycoprotein antigen from Aspergillus fumigatus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;79(3):263–269. doi: 10.1159/000233984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Resnick A., Scribner G. H., Gunasekaran M., Fink J. N. Enzyme profile and immunochemical characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus antigens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Dec;78(6):1166–1173. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Resnick A., Scribner G. H., Kalbfleisch J. H., Fink J. N. Comparison of antigens and serological methods in Aspergillus fumigatus antibody detection. Mykosen. 1984 Jan;27(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1984.tb01981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Ting E. Y., Fink J. N. Immunochemical characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):698–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.698-701.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longbottom J. L., Harvey C., Taylor M. L., Austwick P. K., Fitzharris P., Walker C. A. Characterization of immunologically important antigens and allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;88(1-2):185–186. doi: 10.1159/000234780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra S. K. Antigenic profile of some typical and septate phialide-strains of Aspergillus fumigatus. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(2):91–100. doi: 10.1080/00362178485380161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechura J. E., Kurup V. P., Fink J. N., Calvanico N. J. Antigens of Aspergillus fumigatus. III. Comparative immunochemical analyses of clinically relevant aspergilli and related fungal taxa. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Mar;59(3):716–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechura J. E., Riefel R. S., Daft L. J. Electrophoretic and serological analyses of cytoplasmic antigens from Aspergillus fumigatus during growth of conidia to mature mycelia. J Med Vet Mycol. 1987 Aug;25(4):243–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamame M., Antequera F., Villanueva J. R., Santos T. High-frequency conversion to a "fluffy" developmental phenotype in Aspergillus spp. by 5-azacytidine treatment: evidence for involvement of a single nuclear gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2287–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Pizzo P. A. Nosocomial fungal infections: a classification for hospital-acquired fungal infections and mycoses arising from endogenous flora or reactivation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:517–545. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Reiss E. Current trends in immunodiagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):301–312. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]