Table 4.
Carboamination of aliphatic imides and amides.a
| entry | substrate | product(s) | yieldb(selectivity) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
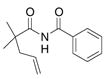
17 |
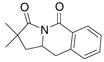
18 |
81% | |
| 2c,d |
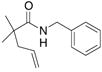
19 |
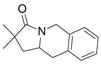
20 |
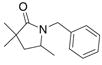
21 |
70%(20:21 = 1.6:2) |
| 3c,e |
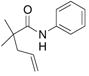
22 |
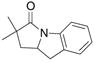
23 |
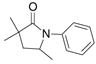
24 |
83%(23:24 = 3.3:1) |
| 4c,e |
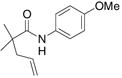
25 |
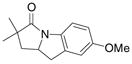
26 |
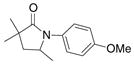
27 |
79%(26:27 = 3.4:1) |
| 5c |
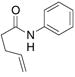
28 |
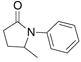
29 |
56% | |
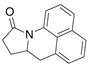
| 6 |
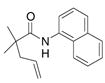
30 |
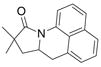
31 |
81% | |
| 7c |
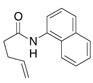
32 |
33 |
74% | |
Conditions. Substrate in DMF (0.1 M) was treated with Cu(EH)2 (3 equiv) and Cs2CO3 (1 equiv). The mixture was heated to 120 °C for 24 h in a pressure tube.
Yields refer to the sum of products isolated by chromatography on SiO2. The remainder of the material was either starting olefin or olefin-isomerized starting material.
Heated to 190 °C.
Reaction run for 72 h.
tbutyl benzene was used as solvent.
