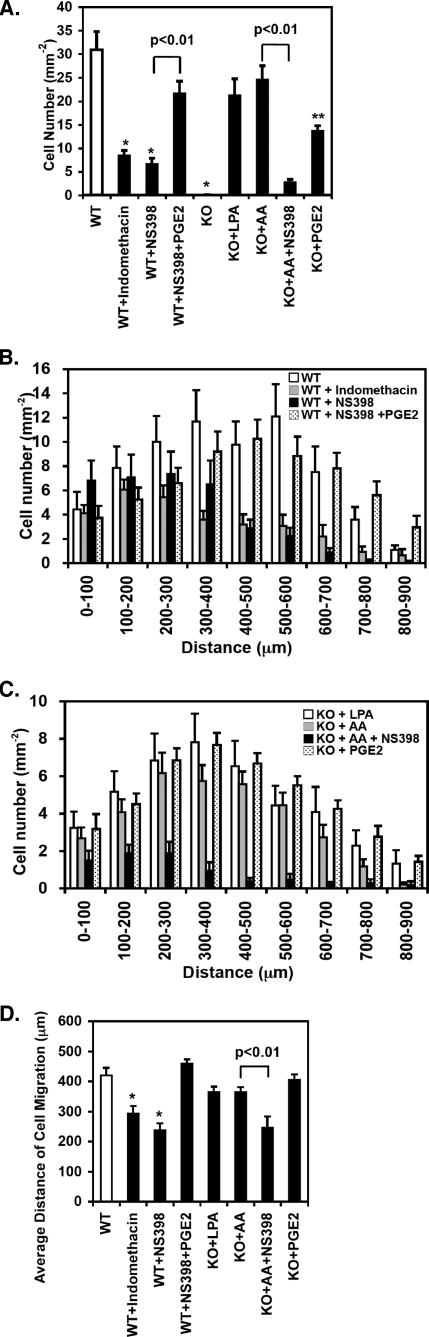
FIGURE 7.
COX-2-specific inhibition prevents AA-mediated rescue of the migration and proliferation of iPLA2β-null SMCs obtained from mouse mesenteric arterial explants. Mesenteric arterial explants were excised from wild-type (WT) and iPLA2β-null (KO) mice, covered with poly-l-lysinecoated glass coverslip, and incubated in the absence or presence of LPA (2 μm), AA (2 μm), or PGE2 (5 μm) with or without the COX-2-specific inhibitor NS-398 (10 μm) or the non-selective COX inhibitor indomethacin (20 μm) in the cell culture medium (replaced at 2-day intervals). Images of tissue fragments with the migrating cells were obtained using a digital microscope (10× air objective) (at 21 days post-isolation), after which migrating and proliferating cells were counted and averaged for each group. The number of cells per tissue fragment was normalized by multiplication by the fraction of dishes containing migrating cells per group (A). The number of cells within the indicated path-independent distance of each cell from the nearest explant edge with standard error bars were measured for each group of wild-type (WT)(B) and iPLA2β-null (KO) cells (C). A summary of the average distance of migration using the data (results) given in B and C ± S.E. is presented in D. Results were obtained from independent preparations from at least three separate animals for each group. *, p < 0.01 when compared with WT control. **, p < 0.01 when compared with KO control.