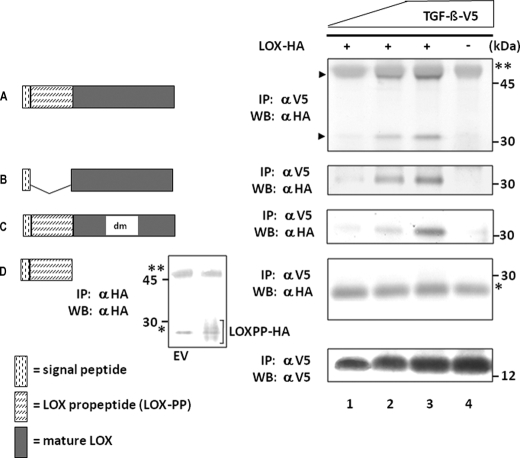
FIGURE 2.
LOX constructs and their binding to TGF-β1 by IP-WB analysis. Four LOX-HA constructs generated, i.e. LOX-HA (A), mature LOX-HA (B), LOX with double mutations (LOXdm-HA) (C), and LOX propeptide (LOXPP-HA) (D), are shown on the left. The binding of each construct to TGF-β1-V5 was analyzed by IP with anti-(α) V5 antibody followed by WB with α HA antibody and shown on right. Expression levels of TGF-β1-V5 are shown by WB with α V5 antibody at the bottom panel on the right. When LOX-HA was expressed, both full-length (50 kDa) and mature LOX-HA (33 kDa) were synthesized (indicated by arrowheads). Note that full-length, mature, and dmLOX-HA showed binding to TGF-β1-V5 in a dose-dependent manner (a–c, lanes 1–3), but no binding was observed for LOXPP-HA (d). The presence of LOXPP-HA (∼28 kDa) in the medium was confirmed by IP-WB analysis with α HA antibody in comparison with the negative control (EV) and is shown in a small inset left to d. LOXPP-HA is indicated by a bracket. IgG heavy (50 kDa) and light (25 kDa) chains are indicated by two and one asterisks, respectively.