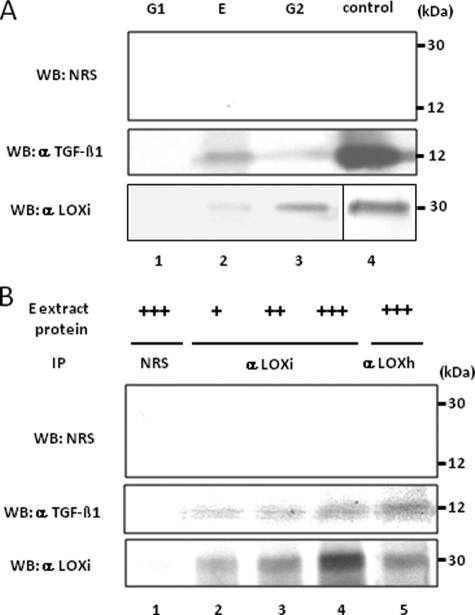
FIGURE 6.
Binding of LOX and TGF-β1 in bone matrix. A, presence of LOX and TGF-β1 proteins in bone matrix extracts. WB analyses were performed with anti-(α) LOXi antibody (lower panel), α TGF-β1 antibody (middle panel), and NRS (upper panel). The immunoreactive bands for LOX and TGF-β1 were detected at the expected molecular weight in E and G2 fraction of bone (lanes 2 and 3) but not in G1 fraction (lane 1). No immunoreactive bands were detected with NRS (upper panel). G, guanidine-HCl; G1, first G extract; E, EDTA extract; G2, second G extract. LOX isolated from bovine aorta by the method reported (75) and rhTGF-β1 were used as positive controls (lane 4). B, LOX-TGF-β1 binding complex in bone E extract. Various amounts of E extract were subjected to IP-WB analysis in combination of α LOXi, α LOXh, α TGF-β1 antibody, or NRS as indicated. Note that immunopositive bands of TGF-β1 are detected in a dose-dependent manner (middle panel, lanes 2–4) when IP was performed with α LOXi. An immunopositive band was also observed when IP was performed with α LOXh antibody (lane 5). No immunoreactivity was detected when NRS was used (upper panel, lanes 1–5, middle/lower panel, lane 1). +, ++, +++, 500, 1000, and 2000 μg, respectively, of E extract protein.