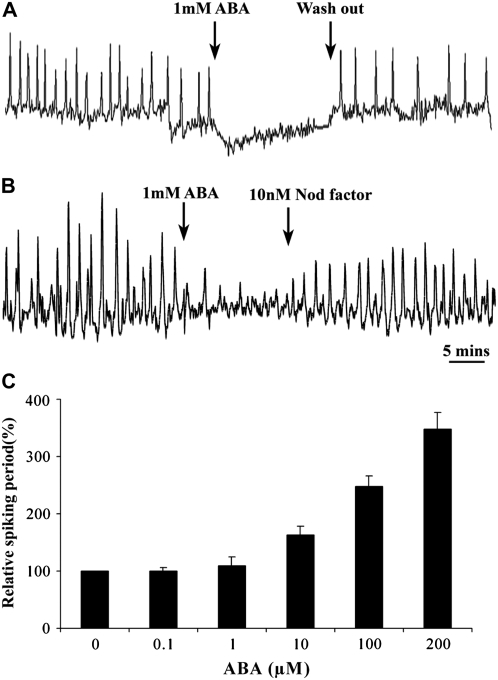
Figure 3.
ABA Modulates Nod Factor–Induced Calcium Spiking.
(A) and (B) Representative calcium traces of M. truncatula root hair cells preinduced with 1 nM Nod factor and secondarily treated with 1 mM ABA. Treatment with ABA inhibits calcium spiking, and this can be recovered following ABA washout in continuous 1 nM Nod factor (A) or by raising the Nod factor concentration to 10 nM (B). Calcium measurements were generated from cameleon transformed plants, and the y axes represent the ratio of cyan fluorescent protein: yellow fluorescent protein (CFP:YFP) in arbitrary units. Error bars represent se.
(C) While 1 mM ABA inhibits calcium spiking, lower concentrations of ABA cause a lengthening of the interval between individual calcium spikes. The period between calcium spikes was averaged from 20 min of spiking in 20 cells per treatment, and this period was standardized relative to no ABA treatment.