Figure 2.
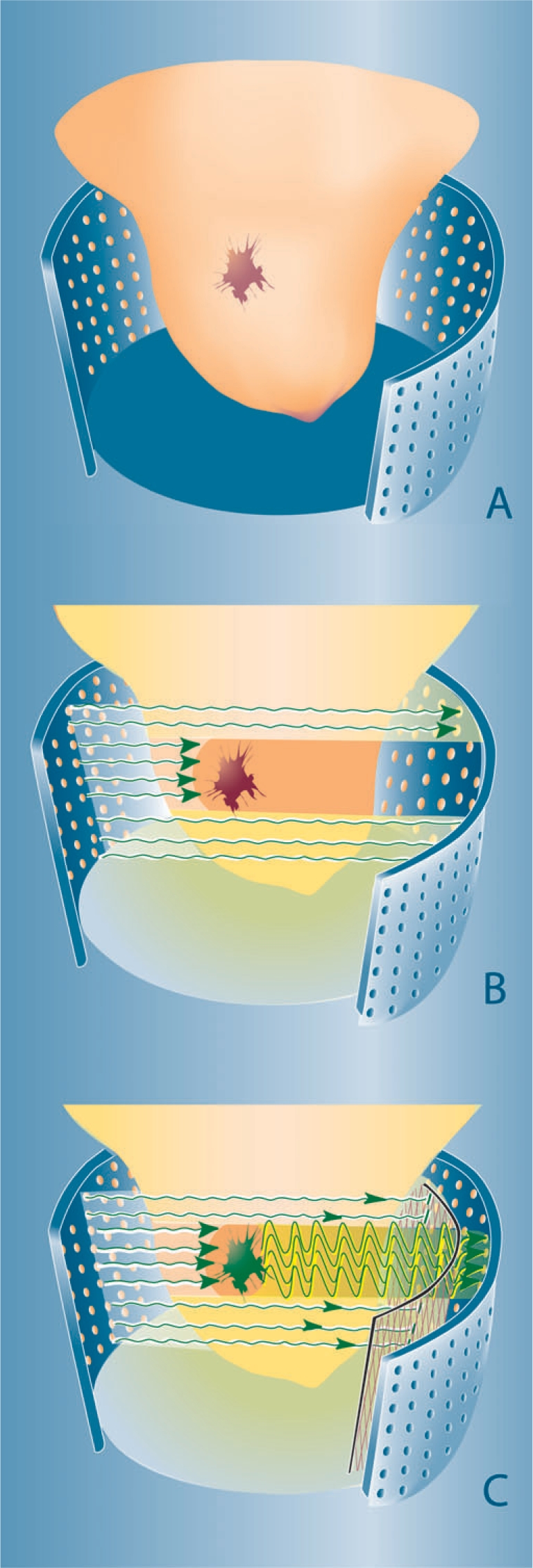
Concepts of optical breast imaging. Optical breast imaging lay-out (A) with source and detector fibres covering the entire breast surface. In optical breast imaging without contrast agent (B) higher absorption by tumour components (predominantly haemoglobin) results in decreased light intensity registered by the detectors. In optical breast imaging with contrast agent (C) a fluorescent probe is administered that ideally accumulates at the tumour site. After excitation, light is emitted at a higher wavelength by this agent and the excitation wavelength is filtered to only detect the fluorescent signal.
