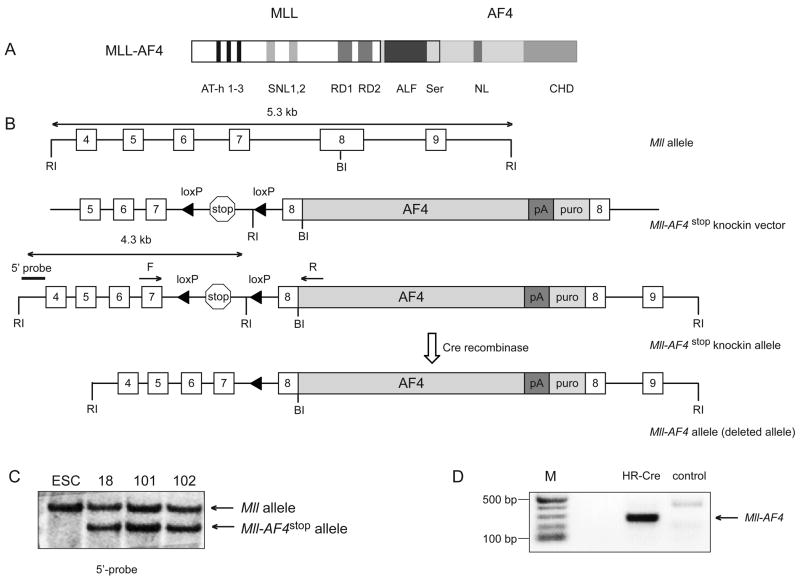
Figure 1. Generation of mice with a conditional Mll-AF4stop allele.
A Schematic representation of the MLL-AF4 fusion protein including a number of protein motifs. AT-hooks (AT-h 1–3); speckled nuclear localization sites (SNL1 and SNL2); transcriptional repression domain consisting of two functional subunits, (RD1) and (RD2); homologous regions among within the AF4/FMR2 family members (ALF); Serine-rich regions that contain a transactivation domain (Ser); nuclear localization signal (NL); C-terminal homology domain conserved between FMR2, AF4 and LAF4 family of transcription factors (CHD). B. A diagrammatic description of the Mll-AF4stop knockin allele. Mll exons are numbered 4 to 9. The poly-adenylation site (pA) and puromycin (puro) resistance cassette is shown. EcoRI (RI) and BamHI (BI) sites and Mll forward (F) and AF4 reverse (R) primers used for Mll-AF4 fusion RNA detection are shown. C. Southern blot analysis of EcoRI-digested genomic DNA from wild-type and targeted ESC, probed with the 5′-probe shown in B. D. RT-PCR analysis of Mll-AF4 transcript expression in total bone marrow from Mll-AF4stop mice retrovirally transduced either with “Hit and run Cre” (HR-Cre) or MSCV-MIG (control). (M) molecular weight marker in basepairs (bp).