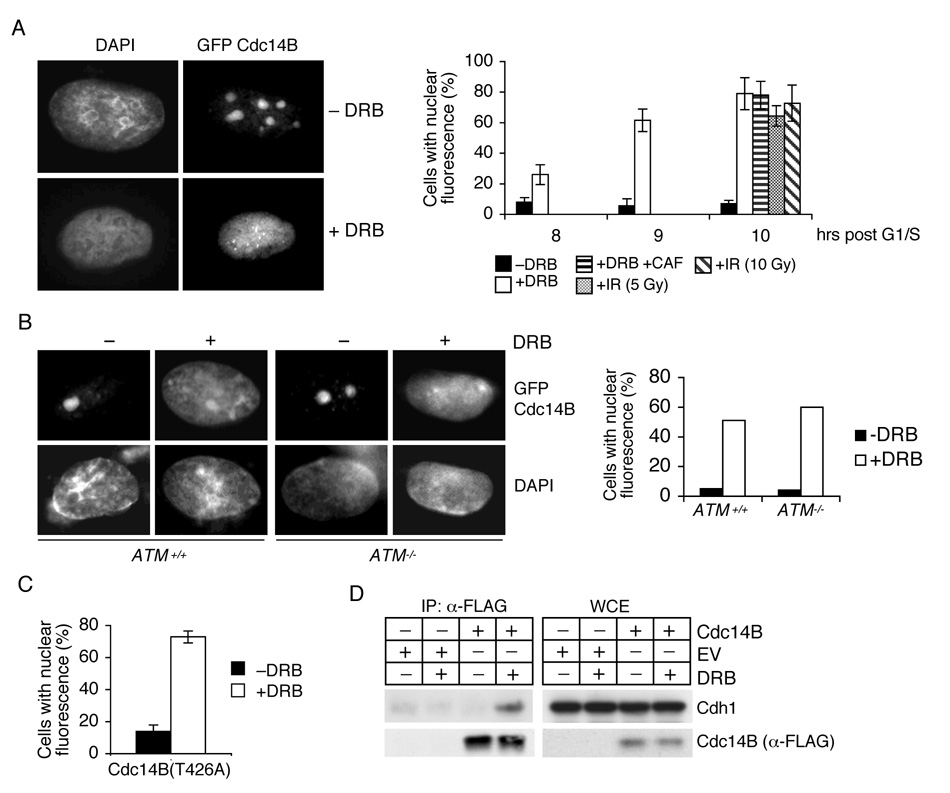
Figure 4. Cdh1 associates with Cdc14B in G2 in response to DNA damage.
(A) Cdc14B moves from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm in response to DNA damage. U2OS cells transfected with a construct expressing GFP-tagged Cdc14B were synchronized as described in (2A) and then either treated with DRB [+/−caffeine (CAF)] or subjected to ionizing radiations (IR). Cells were then collected and analyzed by direct immunofluorescence. Left panels: micrographs of representative cells showing the subcellular localization of Cdc14B. Right panel: Quantification of cells with nuclear Cdc14B fluorescence at the indicated times post pulse with doxorubicin (n=3, ± SD).
(B) Cdc14B translocation to the nucleus is independent of ATM. The experiment was performed as in (A), except that asynchronous ATM+/+ and ATM−/− fibroblasts were used (n=2).
(C) The experiment was performed as in (A), except that GFP-tagged Cdc14B(T426A) was used (n=3).
(D) Cdh1 binds to Cdc14B in a DNA damage-dependent manner. U2OS cells infected with either an empty retrovirus (EV) or viruses encoding FLAG-tagged Cdc14B were synchronized and treated with DRB as described in (A). Cells were collected two hours later, and whole cell extracts (WCE) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG resin. The indicated proteins were detected by immunoblotting.