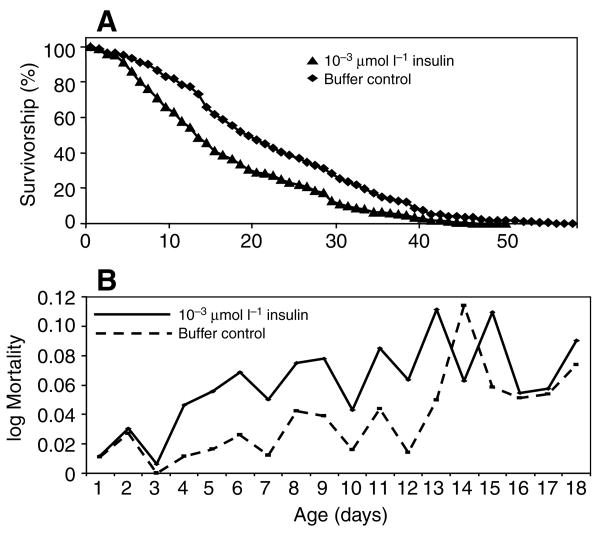
Fig. 2.
Example survivorship curve (A) and mortality rate (B) showing that human insulin provided by artificial bloodmeal increased the mortality of A. stephensi relative to controls. These plots correspond to the data for experiment 3, Table 2. Female mosquitoes were provided with 1.7×10−3 μmol l−1 human insulin or with an equivalent volume of insulin buffer by artificial bloodmeal every Monday, Wednesday and Friday until all insects were dead. Oviposition cups and 10% sucrose pads were provided between bloodmeals. Dead insects were counted and removed daily from treatment and control cartons.