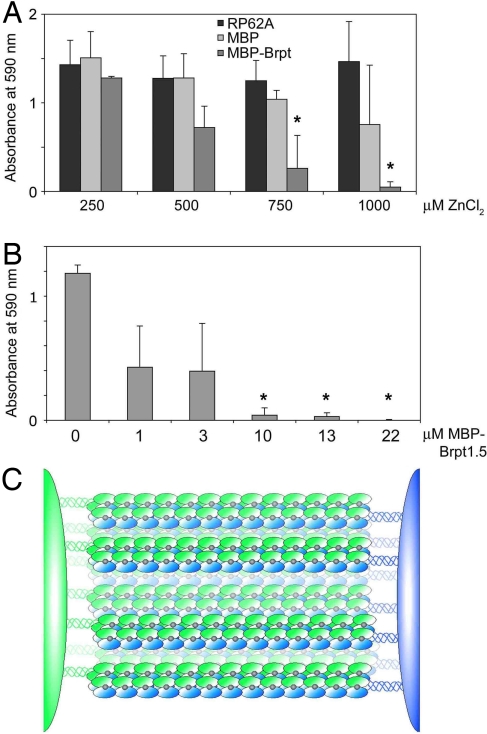
Fig. 4.
Soluble G5 domain inhibits biofilm formation in a dose-dependent manner. (A) Addition of soluble MBP–Brpt1.5 inhibits RP62A biofilms in a dose-dependent manner in the presence of 0.75–1 mM ZnCl2. MBP alone was statistically indistinguishable from untreated control at all concentrations tested. (*, P < 0.05 relative to RP62A control at the relevant Zn2+ concentration; n = 3). (B) Dose−response of biofilm inhibition by MBP–Brpt1.5 at a fixed 1 mM ZnCl2 concentration. (*, P < 0.0005; n = 3). (C) The zinc zipper model for intercellular adhesion in staphylococcal biofilms mediated by zinc-dependent self-association of G5 domains.