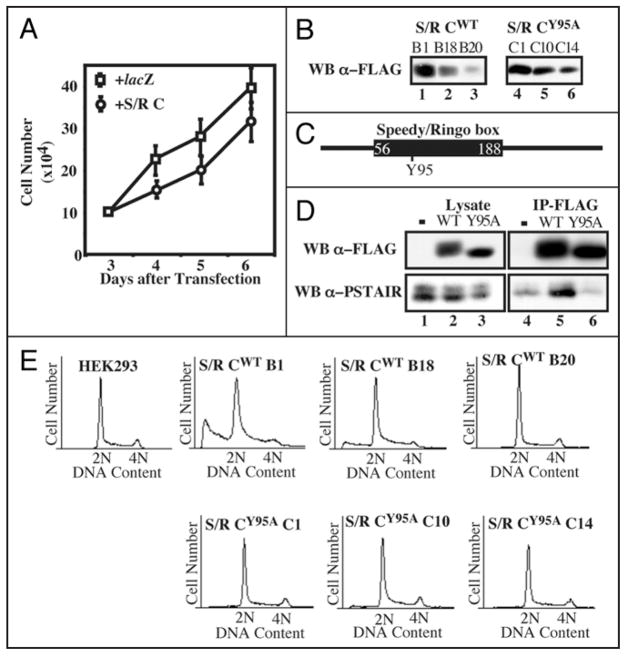
Figure 4.
Effects of overexpression of Speedy/Ringo C on cell growth and the cell cycle. (A) Ectopic expression of Speedy/Ringo C inhibited cell growth. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding lacZ or 3xFLAG-Speedy/Ringo C. The cell number was measured at different times. Values represent the means ± S.E. from three separate experiments. (B) Isolation of HEK293 clones expressing different levels of Speedy/Ringo CWT or Speedy/Ringo CY95A. HEK293 cells were transfected with pcDNA3-3xFLAG-Speedy/Ringo CWT and pcDNA3-3xFLAG-Speedy/Ringo CY95A. Stable clones were selected using G418 and cell lysates were immunoblotted for 3xFLAG-Speedy/Ringo C. (C) Schematic illustration of the conserved Speedy/Ringo box and the position of Tyr-95 in Speedy/Ringo C. (D) The Speedy/Ringo C Y95A mutant was unable to interact with CDKs. HEK293 cells were lysed 48 hours after transfection with pcDNA3, pcDNA3-3xFLAG-Speedy/Ringo CWT, and pcDNA3-3xFLAG-Speedy/Ringo CY95A. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2 agarose. Cell lysates (lanes 1–3) and immunoprecipitates (lanes 4–6) were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against FLAG to detect Speedy/Ringo C (top) and PSTAIRE to detect Cdc2 and Cdk2 (bottom). (E) DNA content in HEK293 cells and selected clones from (D) was determined by flow cytometry of propidium iodide-stained cells.