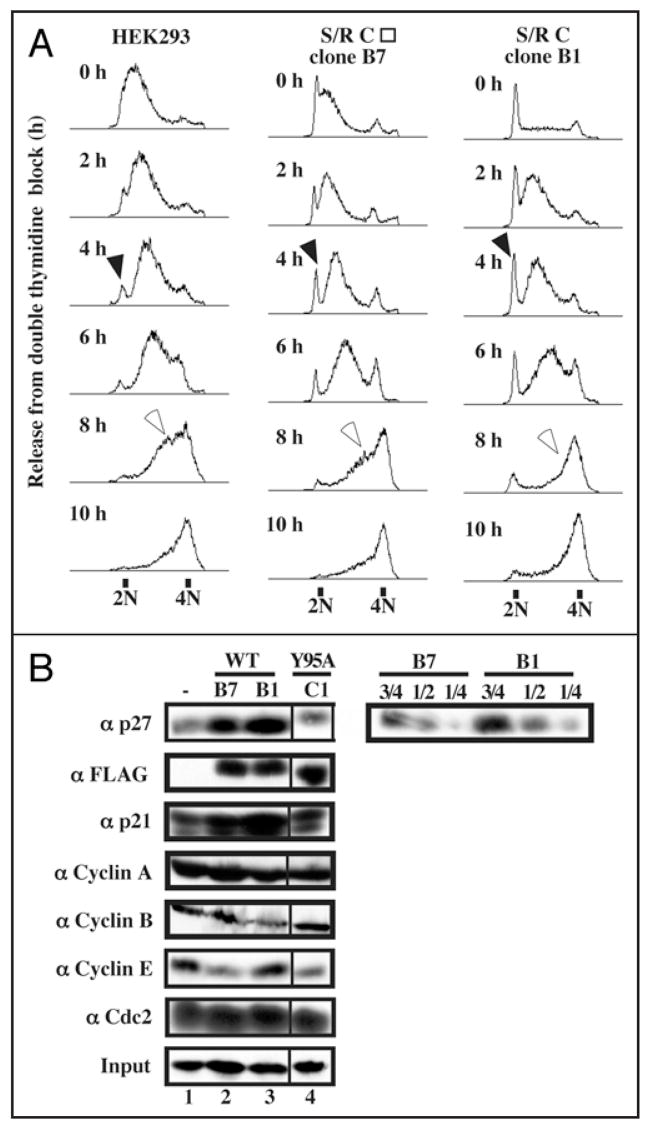
Figure 5.
Overexpression of Speedy/Ringo C slowed the G1-to-S transition and promoted rapid progression through late S phase. (A) HEK293 cells and two Speedy/Ringo C-expressing clones (B1 and B7, whose Speedy/Ringo C level was slightly lower than that of clone B1) were synchronized by a double thymidine block protocol. The cells were released from the thymidine block into medium containing nocodazole and harvested at the indicated times. Cell cycle distributions were analyzed by flow cytometry of propidium iodide-stained cells. Cells delayed at the G1/S boundary are indicated with solid arrowheads; cells in late S phase are indicated with open arrowheads. (B) Immunoblotting analysis of cell cycle regulators in HEK293 cells (lane 1), Speedy/Ringo CWT clone B7 (lane 2), clone B1 (lane 3), and Speedy/Ringo CY95A clone C1 (lane 4). Serial dilutions of proteins from Speedy/Ringo CWT clones B1 and B7 were made to facilitate quantitation of p27 levels between HEK293 cells and Speedy/Ringo CWT clones. Note that the lane 4 samples in the left-hand panels are from a different part of the same autoradiographs as lanes 1–3.