Figure 2.
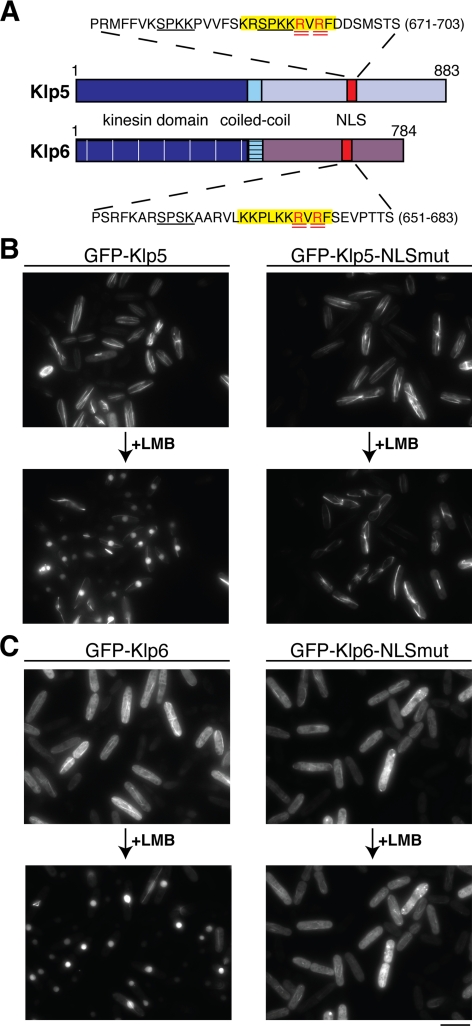
Identification and characterization of Klp5 and Klp6 NLSs. (A) Cartoon depicting Klp5 and Klp6 domains. Dark blue, kinesin domain (note that for simplicity, the N-terminal nonkinesin extensions consisting of −100 amino acid residues are not shown); light blue, coiled-coil; and red, NLS. Amino acid sequences surrounding consensus NLS sequences in Klp5 and Klp6 are highlighted in yellow, and arginine residues mutated to alanines are doubly underlined in red. Underlined sequences in black denote CDK consensus phosphorylation sites. (B and C) Cellular localization of NLS mutants. Δklp5 Δklp6 cells were transformed with plasmids containing GFP-klp5+ (B; left), GFP-klp5-NLSmut (B; right), GFP-klp6+(C; left), GFP-klp6-NLSmut (C; right) and observed by fluorescence microscopy. The same field of cells is shown before and after (60 min) LMB addition. Bar, 10 μm.