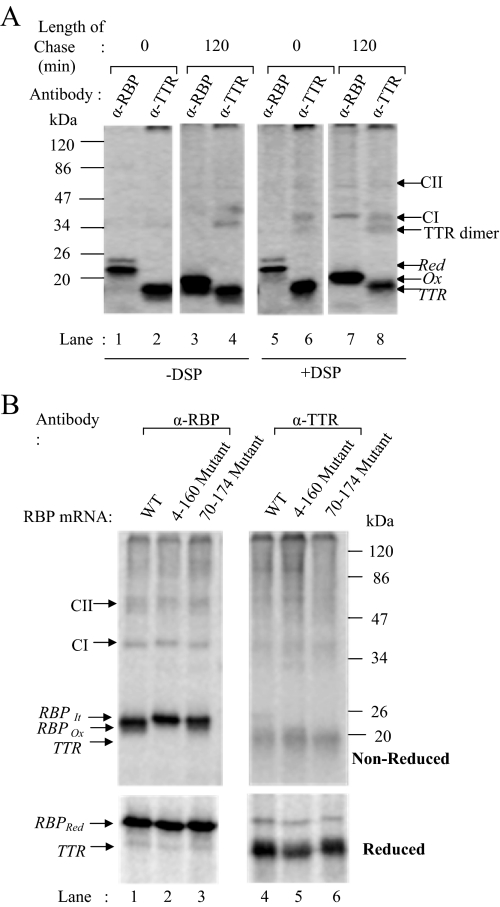
Figure 8.
RBP-TTR assembly in microsomes. (A) RBP and TTR were cotranslated in the presence of microsomes under reducing conditions and disulfide oxidation was carried out as described in text. Samples were withdrawn at 0 h (lanes 1, 2, 5, and 6) and 2 h (lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8) of chase and subjected to cross-linking with DSP. Noncross-linked (left) and cross-linked (right) samples were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against RBP (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7) and TTR (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8) and analyzed by 13% nonreducing SDS-PAGE and fluorography. The positions of reduced and oxidized RBP and TTR are indicated. Bands corresponding to TTR dimer (28 kDa), 1:1 RBP-TTR complex (CI, 35 kDa) and 1:4 RBP-TTR complex (CII, 77 kDa) are indicated by arrows in the gel. (B) Similar procedure was adopted as described above, where WT or mutant RBP mRNA was used for translation. The 2-h chase samples subjected to cross-linking with DSP and immunoprecipitated using antibody against RBP (lanes 1–3) or TTR (lanes 4–6). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by nonreducing or reducing SDS-PAGE (top and bottom, respectively). CI and CII correspond to RBP–TTR complexes described above.