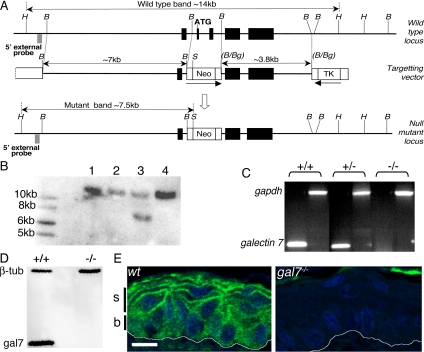
Figure 1.
Establishment of galectin-7 null mutant mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Mouse galectin-7 gene comprises five exons (black boxes). The ATG initiation codon is located in exon 2. The 7-kb fragment of 5′ homology contains exon 1, and the 3.8-kb fragment of 3′ homology contains exons 4 and 5 (see Materials and Methods). H, HindIII; B, BamHI; S, SpeI; Bg, BglII; TK, thymidine kinase gene; and Neo, neomycin resistance gene. (B) Southern blot. G418/Gancyclovir double resistant ES cell clones were picked. Genomic DNA was digested with HindIII/SpeI. The wt (14-kb) and targeted (7.5-kb) fragments were detected with a specific 5′ external probe (A). Clone 3 was used in all subsequent experiments. (C) RT-PCR analysis. Skin RNA was prepared from 2-mo-old littermates obtained by crossing heterozygous animals. Galectin-7 mRNA was amplified using the gal7L/gal7R primers (300-bp product). Control amplification using gadph mRNA was done using gapdh5′/gapdh3′ primers, which gave the expected 1193-bp product (see Materials and Methods). (D) Western blot. Fifteen micrograms of protein extracts prepared from foot pads were loaded on 12% acrylamide gel. After blotting, galectin 7 (14-kDa) and β-tubulin (55-kDa) proteins were detected. (E) Galectin-7 distribution in adult epidermis. Paraffin sections from back skin samples of wt and galectin-7−/− mice were immunostained with anti-galectin-7 Ab. White lines indicate the dermoepidermal junction. B, basal layer; s, suprabasal layers. We noted autofluorescence in cornified layer. Bar, 10 μm.