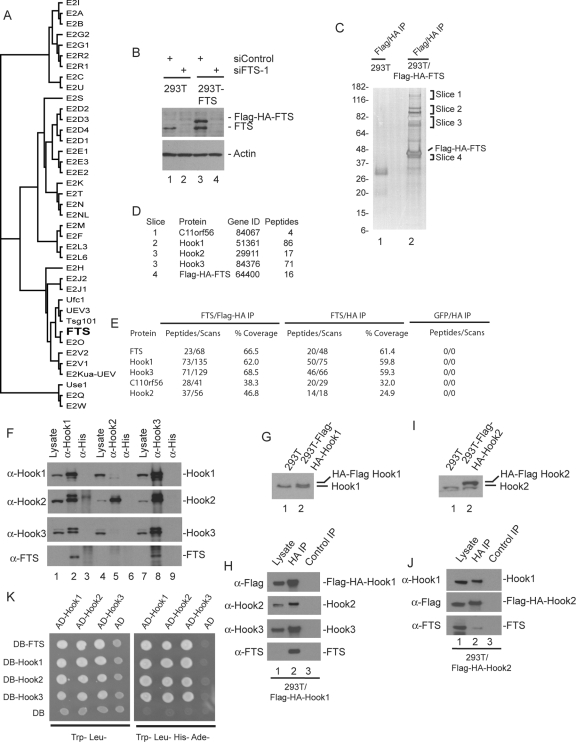
Figure 1.
Proteomic analysis of FTS complexes identifies a new complex containing Hook proteins and C11ORF56/p107FHIP. (A) Phylogenetic tree of the human E2 conjugating family, generated using ClustalW. The variant E2 protein FTS lacking the active site cysteine residue found in catalytically active E2 enzymes is shown in bold. (B) Immunoblot analysis of extracts from HEK293T cells or HEK293T cells stably expressing FLAG-HA-FTS from an MSCV-based retrovirus by using anti-FTS antibodies. To demonstrate the specificity of the antibodies, cells were previously transfected with control siRNA or an siRNA targeting FTS. Blots were stripped and reprobed with actin as a loading control. (C and D) SDS-PAGE and mass spectral analysis of FLAG-HA-FTS complexes. Tandem anti-FLAG/anti-HA immune complexes from HEK293T cells or HEK293T/FLAG-HA-FTS cells separated on a 4–20% gradient SDS-PAGE gel and stained with silver (C). The indicated gel slices were analyzed by mass spectrometry (D). The number of independent peptides identified for each protein is shown. These proteins were not found in the negative control (lane 1). (E) LC/MS/MS analysis of tandem and single HA purified FLAG–HA–FTS complexes. Tandem (FLAG-HA) or single anti-HA purified complexes derived from four 15-cm dishes of cells were eluted with HA peptide, precipitated with trichloroacetic acid to remove the eluting peptide, trypsinized, and subjected to LC/MS/MS. Cells expressing FLAG-HA-GFP were used in parallel as a control. The number of independent peptides as well as the total number of scans for these peptides is indicated, as well as the coverage of each protein. (F) Extracts from HEK293T cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Hook1, anti-Hook2, or anti-Hook3 antibodies (or anti-His tag antibodies as a negative control), and complexes were subjected to immunoblotting by using the indicated antibodies. Lysates (5% of input) were included in the blot. Note that under these conditions, the crude FTS antisera used in this experiment does not readily detect FTS in crude cell extracts, and FTS is highly enriched in the anti-Hook1 and Hook3 immune complexes. (G) HEK293T cells stably expressing FLAG-HA-Hook1 were generated and extracts examined by immunoblotting using antibodies against Hook1. (H) Anti-HA or control immune complexes from HEK293T/FLAG-HA-Hook1 cells were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies, with lysate (5%) as a positive control. Note that under these conditions, the crude FTS antisera used in this experiment does not readily detect FTS in crude cell extracts, and FTS is highly enriched in the anti-Hook1 and Hook3 immune complexes. (I) HEK293T cells stably expressing FLAG-HA-Hook2 were generated and extracts examined by immunoblotting using antibodies against Hook2. (J) Anti-HA or control immune complexes from HEK293T/FLAG-HA-Hook2 cells were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies, with lysate (5%) as a positive control. In this experiment, affinity-purified anti-FTS was used, which was capable of detecting FTS present in cell extracts (lane 1). (K) Two hybrid analysis of FTS and Hook proteins. The indicated open reading frames were cloned into either pDB or pAD vectors by using empty vectors as negative controls (see Materials and Methods) and transformed into PJ69-4A cells. Cells were plated on either Trp−, Leu− media to select for plasmids or on Trp−, Leu−, His−, Ade− to demonstrate the two hybrid interaction.