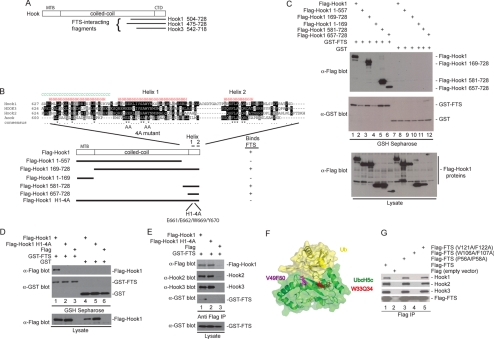
Figure 2.
Anatomy of the FHF complex. (A) A two-hybrid screen for proteins that interact with FTS by using a HeLa cells activation domain library was performed in PJ69-4A cells. Two Hook1 clones and one Hook3 clone were recovered. The location of the FTS-interacting clones on the Hook domain structure is shown. (B) Schematic of Hook1 fragments generated along with the sequence of the C-terminal FTS interacting region of Hook proteins and the results of binding studies. The positions of 2 helices in the C terminus of Hook1 (as determined using the JPRED secondary structure prediction tool; http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/∼www-jpred/) are shown. The positions of mutations in helix 1 within the Hook14A mutant are indicated by “A” for alanine. (C) A C-terminal fragment of Hook1 is necessary and sufficient for interaction with FTS. HEK293T cells were transfected with vectors expressing the indicated proteins and after 48 h, cell extracts were generated and incubated with GSH-Sepharose. Bound proteins and control lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) The Hook14A mutant cannot bind FTS. Experiments were performed as described in C. (E) The Hook14A mutant maintains interaction with Hook2 and Hook3. HEK293T cells were transfected with vectors expressing the indicated proteins and after 48 h, cell extracts were generated and incubated with anti-FLAG (M2) resin. Bound proteins and control lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (F) A structure of UbcH5 bound to ubiquitin (PDB code: 2fuh), showing the residues in UbcH5 that correspond structurally to the W106/F107 and V121/F122 residues mutated in FTS, based on sequence alignments using ClustalW2 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/index.html). (G) FTSW106AF107A fails to interact with Hook proteins. Plasmids expressing the indicated FLAG-tagged wild-type or mutant FTS proteins were transfected into HEK293T cells, and after 48 h, cell extracts were generated and incubated with anti-FLAG (M2) resin. Bound proteins and control lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.