Figure 1.
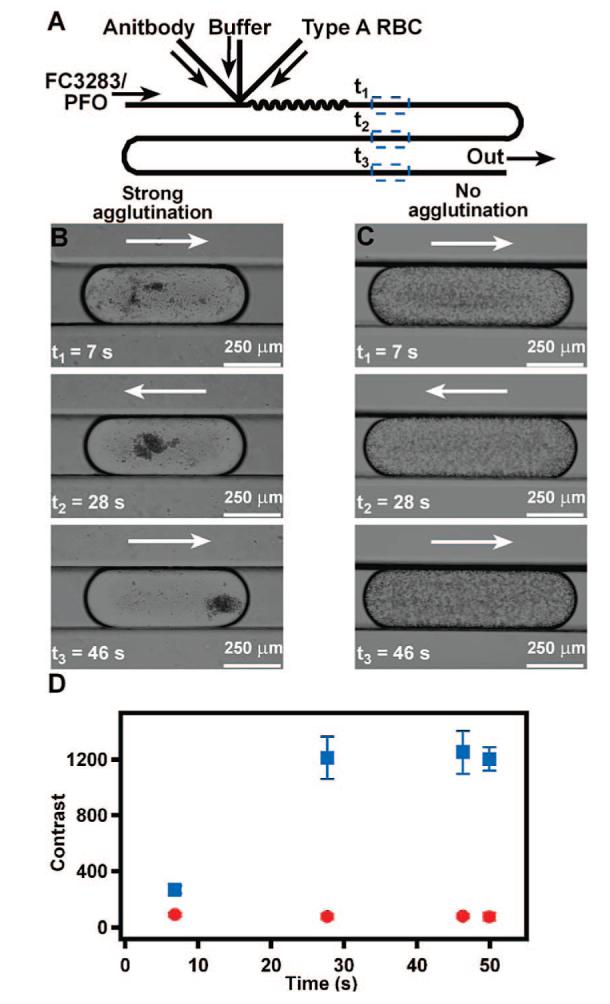
Plug-based microfluidic agglutination assay to distinguish type A from type B RBCs. (A) A schematic drawing shows the device design used for the agglutination assay. (B, C) Time-lapse bright-field microphotographs of representative plugs containing antibody, TRIS buffer, and type A RBCs show that type A RBCs agglutinate in the presence of anti-A (B) but not in the presence of anti-B (C). (D) A graph quantifies the change in contrast of plugs, indicative of agglutination, of type A RBCs exposed to anti-A (blue squares) or anti-B (red circles) (n = 3 plugs). Contrast analysis was performed by using ImageJ. Arrows indicate the direction of fluid flow.
