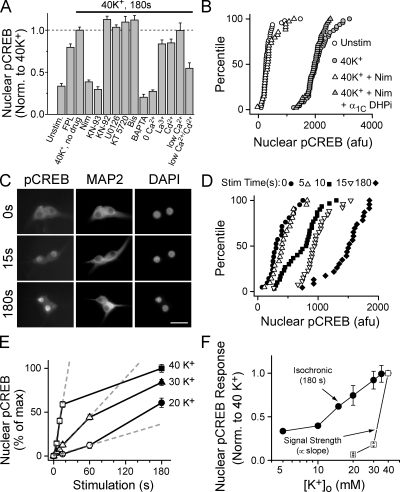
Figure 1.
Strength of signaling to CREB in SCG neurons: dependence on activation of L-type Ca2+ channels and a CaM kinase pathway. (A) Nuclear pCREB levels after a 3-min, 40-mM K+ or FPL 64176 stimulation. Drugs (KN-93, CaMK inhibitor; KN-92, inactive congener of KN-93; U0126, MEK inhibitor; KT 5720, PKA inhibitor; Bis [bisindolylmaleimide I], PKC inhibitor) were added 1 min before stimulation. Some cultures were preloaded with 100 μM BAPTA-AM for 30 min at 37°C, stimulated in 0 mM of extracellular Ca2+ and EGTA (0 Ca2+) or 100 μM Ca2+ and no EGTA (low Ca2+), and/or stimulated in 200 μM La3+ or Cd2+ after preincubation for 1 s. Data are from two or more experiments of >40 neurons each. (B) Cumulative histograms of pCREB levels in individual neurons from a representative experiment. Cells stimulated for 3 min as indicated. Infecting cells with adenovirus expressing dihydropyridine-insensitive L-type Ca2+ channel (DHPi) rescued signaling to CREB. (C–E) Data from a representative experiment. Cells were either mock stimulated in 5-mM K+ Tyrode's (t = 0) or stimulated with solutions containing 20, 30, or 40 mM K+ for the time indicated, placed back in 5 mM K+ solution, and then fixed at 3 min. (C) 5–d in vitro SCG neurons stained for pCREB and MAP2; nuclei counterstained with DAPI. Bar, 50 μm. (D) Cumulative histograms of pCREB levels from individual neurons. (E) Mean pCREB levels plotted against stimulation time; [K+] as indicated. Dashed lines are linear fits of initial data points; slope used as index of CREB signal strength. (F) Isochronic nuclear pCREB levels measured at 3 min (•); CREB signal strength (□), measured as in E. Isochronic data from three independent experiments, except the 10- and 15-mM K+ data are the mean of >15 cells from a single duplicate experiment. Error bars represent SEM.