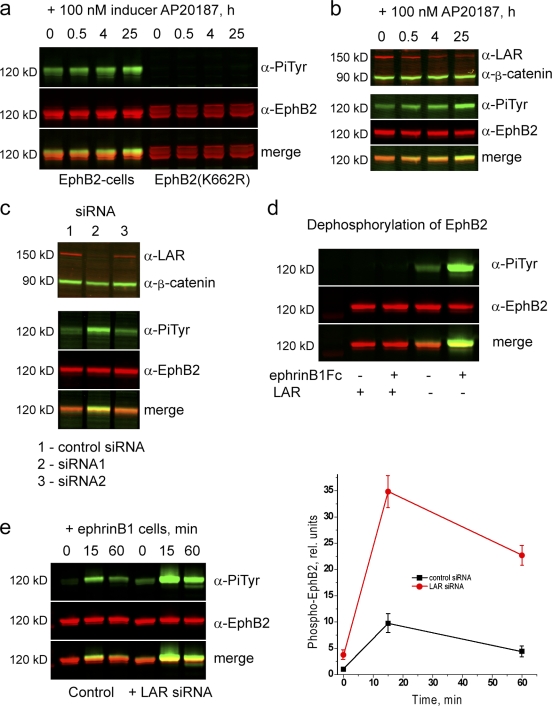
Figure 4.
Role of LAR in dephosphorylation of EphB2. Immunoprecipitations and Western blot analyses were performed to analyze mechanisms that may affect the level of EphB2 phosphorylation. (a) Time course of the effect of iFGFR activation on the phosphorylation of EphB2 (left) or kinase-inactive EphB2 (K662R; right). Kinase-inactive EphB2 is not phosphorylated after iFGFR activation. (b) After iFGFR activation, the expression level of the receptor tyrosine phosphatase LAR progressively decreases (top), concurrent with the increase in baseline EphB2 phosphorylation (bottom). (c) siRNA-mediated knockdown of LAR in EphB2 cells (lane 2) leads to increased baseline phosphorylation of EphB2 in comparison with control siRNA (lane 1). An siRNA that causes less of a decrease in LAR has a smaller effect on EphB2 phosphorylation (lane 3). (d) Immunoprecipitated EphB2 (with or without prior activation by ephrinB1) was incubated with or without the cytoplasmic domain of LAR before Western blot analysis. There is a major decrease in EphB2 phosphorylation after incubation with LAR (left) compared with controls not incubated with LAR (right). (e) The time course of ephrinB1-induced phosphorylation of EphB2 was determined with (left) or without (right) prior knockdown of LAR. The results are shown quantitated in the graph on the right. Knockdown of LAR leads to a major increase in the ephrinB1-induced phosphorylation of EphB2. Error bars indicate range (n = 3). PiTyr, phosphorylated tyrosine.