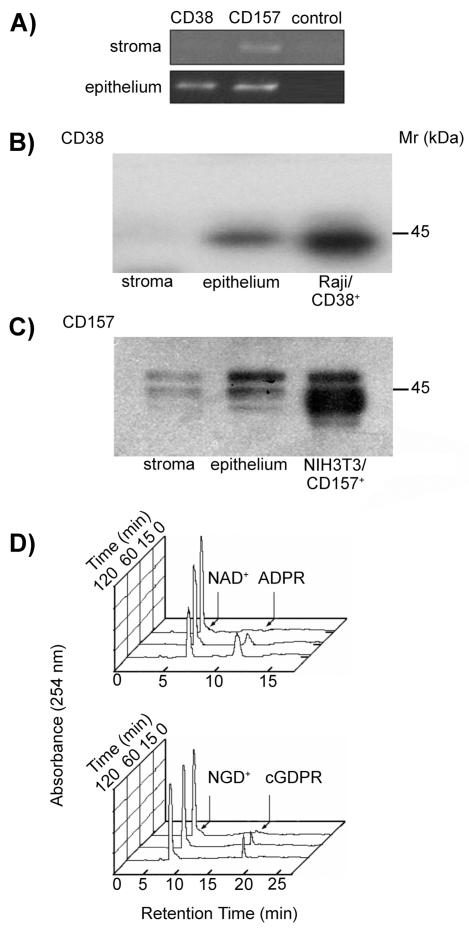
Figure 2.
Biochemical analysis of the CD38 and CD157 molecules expressed by human corneal cells. (A) RT-PCR profile of CD38 and CD157 transcripts in corneal cells. PCR products were amplified from cDNA obtained from epithelial and stromal cells using CD38- or CD157-specific primer sets. Negative controls lacking cDNA template were used to rule out contamination. (B–C) Western blot analysis of corneal stromal and epithelial proteins immunoprecipitated with mAbs to CD38 and CD157. Precipitates of epithelial and stromal cells from biopsied corneas with anti-CD38 (IB4, IgG2a) or with anti-CD157 (SY/11B5, IgG1) mAbs were analyzed by 4% to 12% SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions and blotted onto PVDF membranes. Proteins with Mr of 45-kDa were immunodetected in the corneal epithelia and control Raji (CD38+) cells when blots were probed with anti-CD38 (AT13/5, IgG1) mAb and developed by ECL (B). Proteins with Mr of 42- to 45-kDa were immunodetected in the stroma and corneal epithelia when blots were probed with anti-CD157 (SY/11B5, IgG1) mAb and developed by ECL (C). NIH-3T3/CD157+ transfectants were used as positive control. Isotype-matched irrelevant mAbs were used as negative controls. (D) Ectoenzyme activity molecules assessed in epithelial corneal cells. Cells were incubated with 0.2 mM NAD+ or NGD+ at 37°C and samples collected after 0, 15, 60, and 120 min incubations. NADase (upper panel) and GDP-ribosyl cyclase (lower panel) enzymatic activities were determined by HPLC. Raji (CD38+) cells and NIH-3T3/CD157+ transfectants were used as positive controls. K562 (CD38−) cells and NIH-3T3 mock transfectants were the negative controls.