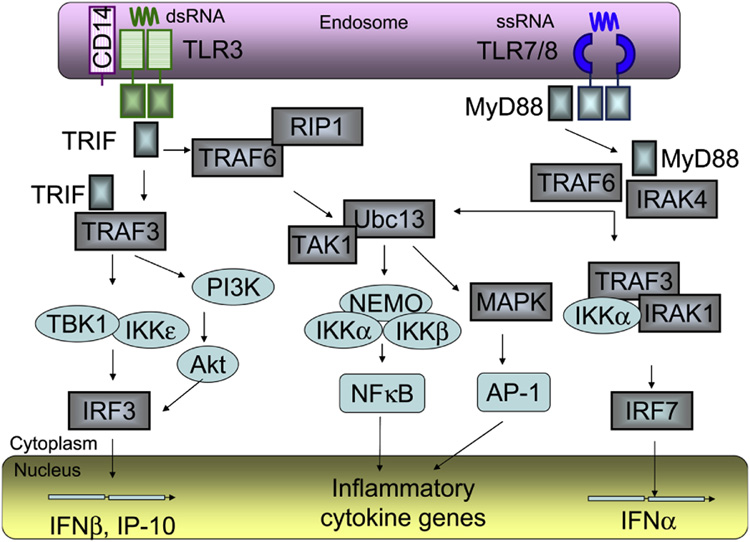
Figure 2. TLR3 and TLR7/8 signaling.
Following stimulation with single stranded (ss) RNA, TLR7/8 recruit MyD88, IRAKs and TRAF6 to activate 2 distinct pathways. When MyD88, IRAKs and TRAF6 recruit Ubc13/TAK, the TAK1 complex then activates the IKK complex, composed of IKKα, IKKβ and IKKγ/NEMO, which catalyzes phosphorylation of IκB proteins and subsequent translocation of NFκB to the nucleus. TAK1 also activates the MAPK pathway, which mediates AP-1 activation. NFκB and AP-1 control the expression of genes encoding inflammatory cytokines. When MyD88, IRAKs and TRAF6 recruit TRAF3, IRAK1 and IKKε into a complex, IRF7 is directly phosphorylated by IRAK1 IKKε , and then translocated to the nucleus to induce expression of IFNα and IFN-inducible genes. Upon interaction with double stranded (ds) RNA, TLR3 recruited TRIF and interacts with TBK1 and IKKε, or activates the PI3K/Akt complex, which both mediate phosphorylation of IRF3. The phosphorylated IRF3 dimerizes and is translocated to the nucleus to induce expression of IFNβ and IFN-inducible genes, including IP-10. TRIF also interacts with TRAF6 and RIP1, which mediate NFκB activation. TLR3 and TLR7/8 are located in endosomes, all signaling events occur in the cytoplasm, while activated transcription factors IRF3, IRF7, NFκB and AP-1 act on the genes within the nucleus. The cellular compartments are not scaled.