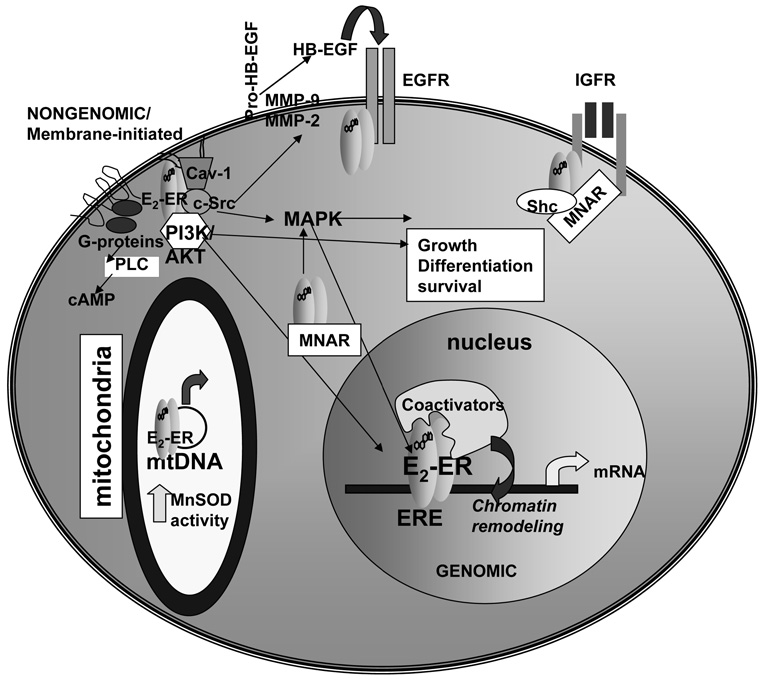
Figure 1. ERα and ERβ have genomic and nongenomic/membrane initiated activities.
As reviewed in the text, ERα and ERβ are located in the cytoplasm and nucleus, within caveolae in the plasma membrane and within mitochondria. For genomic (nuclear) ER activity, E2 binds and activates ER causing dimerization, ERE binding (or interaction with other transcription factors bound to DNA, not shown), coactivator recruitment, chromatin remodeling, and increased transcription in the nucleus. For nongenomic/membrane initiated estrogen signaling, E2 binds ER in caveolae in the plasma membrane. ER interacts with G-proteins, the p85 subunit of PI3K, with c-Src, and caveolin-1 (Cav-1) to initiate PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling cascades. In the cytoplasm, ER interacts with MNAR and Shc which play a role in the nongenomic activities of ER. ER interacts with the EGF- and IGF-1 receptors in plasma membranes. ER in mitochondria interact with the D-loop of mtDNA and directly increase MnSOD activity.