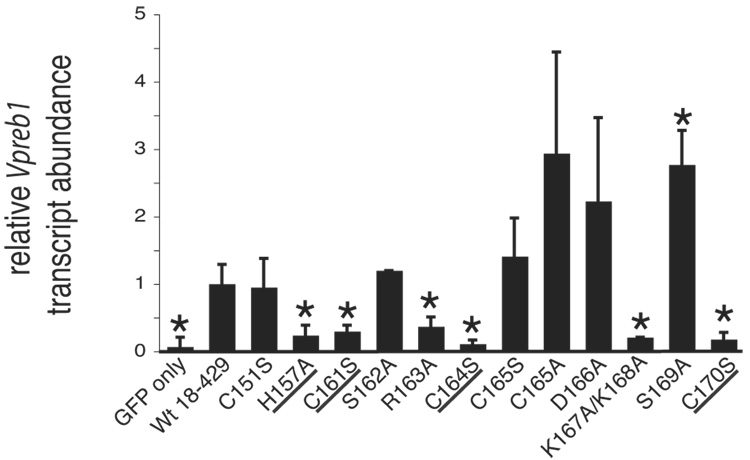
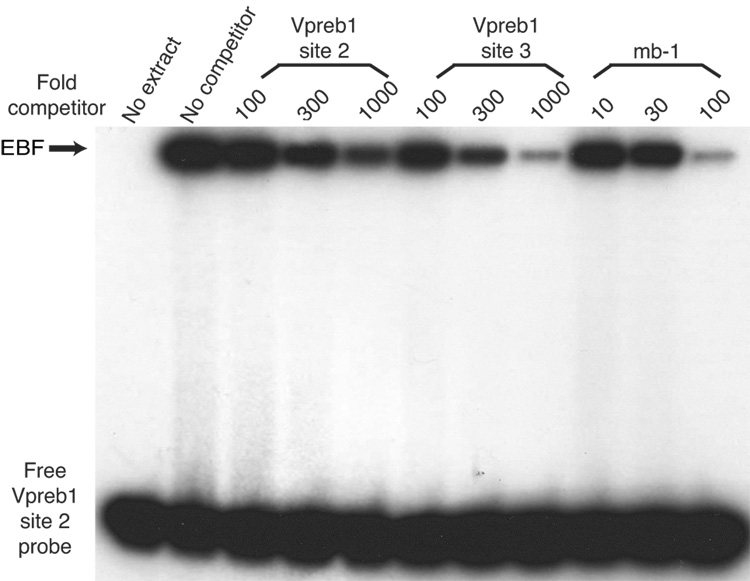
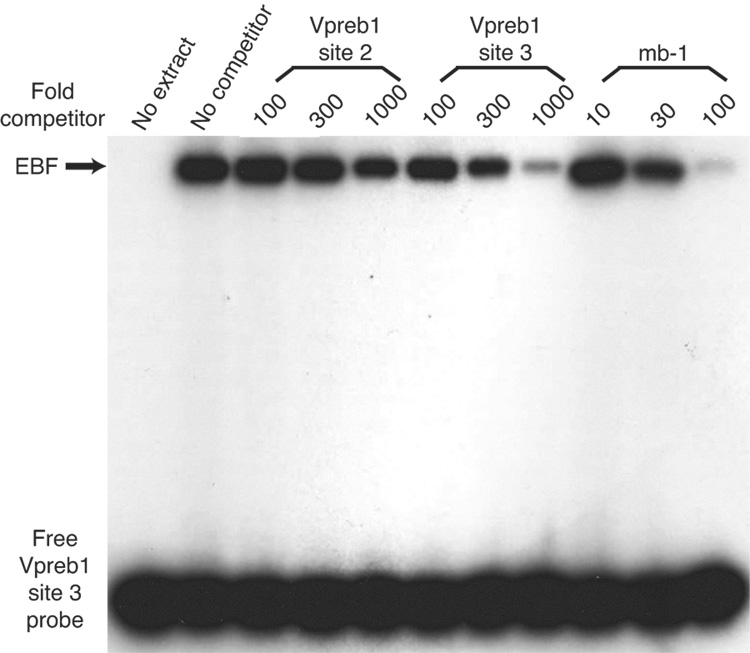
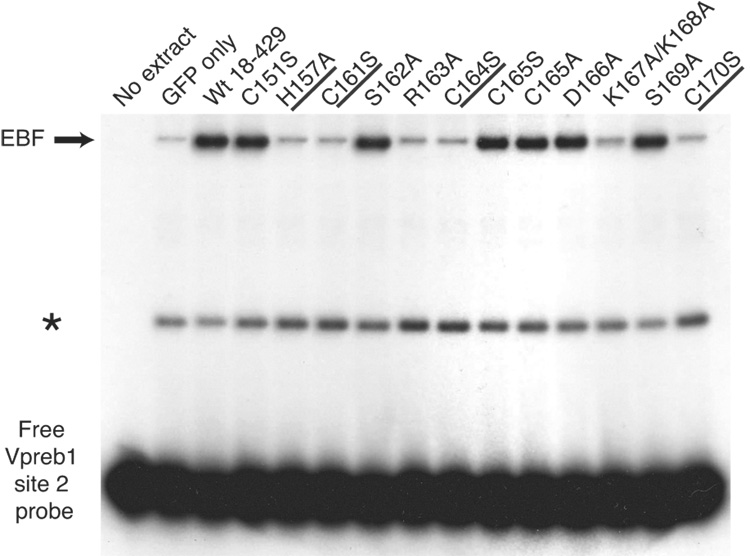
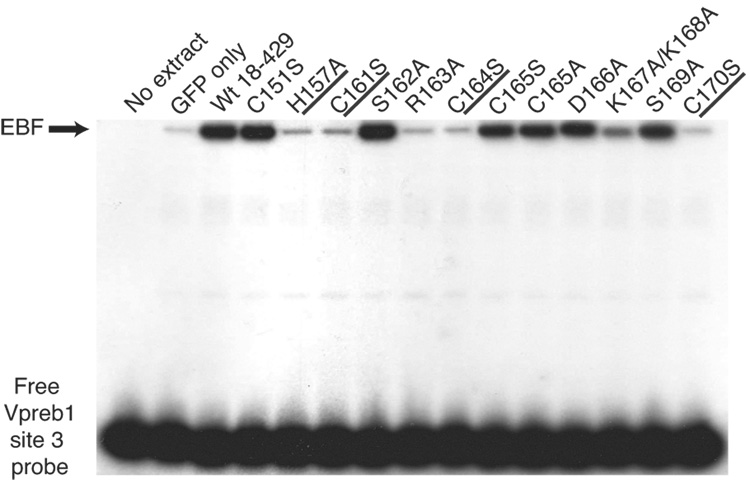
Fig. 3.
Quantitation of Vpreb1 transcripts and DNA binding of the Vpreb1 promoter by wild type and mutated EBF: Zn knuckle mutations. (A) qPCR of Vpreb1 mRNA isolated from µM.2.21 cells infected to express wild type and mutated EBF proteins. Data include mean +/− s.d of three independent experiments. Amounts of Vpreb1 expression from cells expressing wild type EBF were set to one for this experiment (n=3). (B–C) Binding of Vpreb1 site 2 (B) or site 3 (C) by recombinant EBF(18–429). Recombinant EBF (18–429) was incubated with the 32P-labeled Vpreb1 site 2 probe and site 3 (at 3nM or 1.2nM, respectively) in the presence or absence of increasing amounts of Vpreb1 or control mb-1 competitors as shown. (D–E) EMSA of binding of the murine Vpreb1 site 2 (D) or site 3 (E) probe by whole cell extracts of cells infected to express wild type or mutated EBF proteins. *Endogenous complex unrelated to EBF. In (D) and (E), DNA binding and EMSA were performed exactly as in Fig.2C.