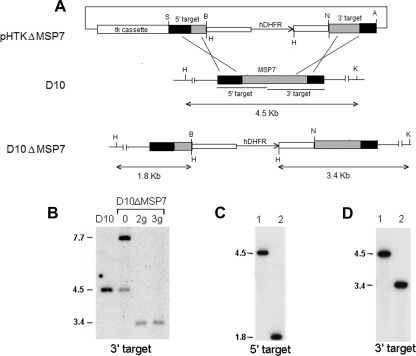
FIG. 1.
Disruption of Plasmodium falciparum D10 msp7 gene. (A) Schematic representation of the knockout plasmid construct (pHTKΔMSP7), the msp7 locus of the parental parasite line (D10), and the resultant msp7 knockout parasite (D10ΔMSP7) lines. The plasmid construct carries a viral thymidine kinase gene cassette (tk cassette) for negative selection with ganciclovir and an hDHFR cassette to insert into the D10 msp7 locus. Insertion of the hDHFR cassette by double homologous recombination within the 5′ and 3′ target regions of msp7 changes the hybridizing KpnI-HindIII restriction fragment sizes from 4.5 kb to 1.8 (with the 5′ target probe) or 3.4 kb (with the 3′ target probe). Relevant restriction sites—AvrII (A), BamHI (B), HindIII (H), KpnI (K), NcoI (N), and SacII (S)—are shown. (B) Southern hybridization of genomic DNA from D10 and transfected parasites digested with KpnI and HindIII and probed with msp7 3′ target probe. Lanes show transfected parasites (0) and ganciclovir-selected parasites after second (2g) or third (3g) WR22910 cycling. The signal at 7.7 kb in lane 0 corresponds to episomal DNA. (C and D) Hybridization analysis of genomic DNA from D10 (lane 1) or the D10ΔMSP7 clone (lane 2) with 5′ or 3′ target DNA probes, respectively. Molecular sizes of hybridizing DNA fragments are indicated.