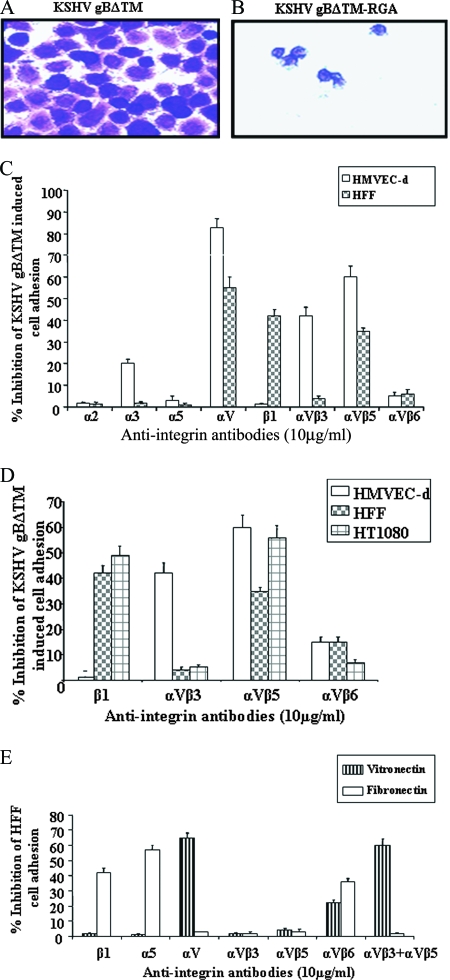
FIG. 1.
Role of integrins in KSHV gB-mediated cell adhesion. (A and B) Maxisorp plates were coated with different concentrations of purified gBΔTM and gBΔTM-RGA in PBS (2 μg/ml; 100 μl/well) overnight at 4°C. The plates were washed and blocked with 1% BSA-PBS, and adhesion assays were performed (80). The adhering cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, washed, and stained with crystal violet. Shown is a photomicrograph of HFF adhering to gBΔTM and gBΔTM-RGA proteins. (C and D) Adhesion of HMVEC-d, HFF, and HT1080 cells to gBΔTM in the presence of anti-integrin antibodies. The cells were incubated with anti-integrin antibodies in 0.1% BSA-serum-free DMEM for 45 min on ice before being seeded onto gBΔTM-coated wells. The crystal violet-stained adhering cells were extracted with 0.1 M sodium citrate and quantified by measurement of the absorbance at 595 nm. Each experiment was done in duplicate, and each bar represents the average plus the standard deviation (SD) of three experiments. (E) Specificities of anti-integrin antibodies inhibiting cell adhesion. HMVEC-d, HFF, and HT1080 cells were incubated with anti-integrin antibodies (10 μg/ml) for 45 min on ice before being seeded in fibronectin- or vitronectin-coated wells. The results with HFF are shown. Each experiment was done in duplicate, and each bar represents the average plus SD of three experiments.