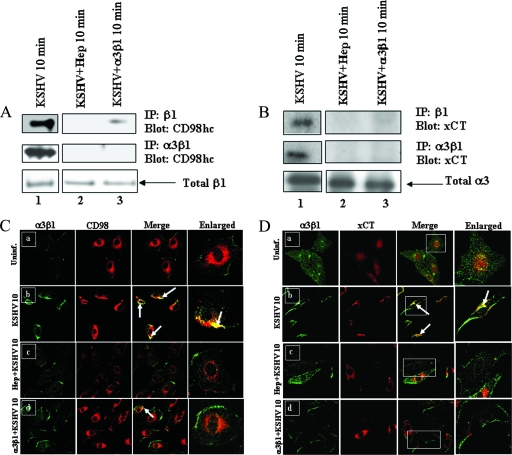
FIG. 5.
Soluble α3β1 and heparin inhibit CD98/xCT association with integrins in KSHV-infected HMVEC-d. Serum-starved HMVEC-d were infected for 10 min with untreated KSHV, KSHV preincubated (37°C for 1 h) with 100 μg heparin sulfate, or KSHV preincubated (37°C for 1 h) with 10 μg of soluble α3β1 at an MOI of 10. (A and B) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-β1 integrin antibody (top) or anti-α3β1 integrin antibody (middle). The immunoprecipitated proteins were Western blotted and probed for CD98hc (A) or for xCT (B). The membranes were reprobed with anti-β1 integrin antibodies (A, bottom), and equal quantities of total cell lysates were probed with anti-α3 integrin antibodies (B, bottom). (C and D) Confocal analysis of α3β1 colocalization with CD98/xCT in KSHV-infected cells. Serum-starved HMVEC-d were infected with untreated KSHV, KSHV preincubated (37°C for 1 h) with 10 μg of soluble α3β1, or KSHV preincubated (37°C for 1 h) with 100 μg heparin for 10 min at an MOI of 10. Uninfected and infected cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100, blocked, and incubated with anti-CD98, anti-xCT, or anti-α3β1 primary antibodies. The cells were then stained with Alexa 488-labeled secondary antibodies for α3β1 (green) or Alexa 594-labeled secondary antibodies for CD98 (red) or xCT (red). (C) Colocalization of α3β1 (green) with CD98 (red) in uninfected (Uninf.) (a), untreated KSHV-infected (b), heparin-treated KSHV-infected (c), and soluble-α3β1-treated KSHV-infected (d) cells. (D) Colocalization of α3β1 (green) with xCT (red) in uninfected (a), untreated KSHV-infected (b), heparin-treated KSHV-infected (d), and soluble-α3β1-treated KSHV-infected (c) cells. The arrows indicate colocalization of proteins. Magnification, ×60. The boxed areas are enlarged in the rightmost column.